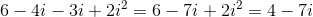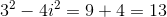Basic Operations with Complex Numbers - Algebra 2
Card 0 of 360

Find  .
.
Find 
Tap to see back →
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the numerator's complex conjugate.

Reduce/simplify.
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the numerator's complex conjugate.
Reduce/simplify.
Simplify: 
Simplify:
Tap to see back →
Distribute the minus sign:

Combine like terms:

Distribute the minus sign:
Combine like terms:
Select the complex conjugate of  .
.
Select the complex conjugate of 
Tap to see back →
 can be restated in standard complex number form as
can be restated in standard complex number form as
 .
.
The complex conjugate of a complex number  is
is  , so the complex conjugate of
, so the complex conjugate of  is
is  , which is equal to
, which is equal to  . Therefore,
. Therefore,  is the complex conjugate of
is the complex conjugate of  .
.


The complex conjugate of a complex number 






Select the complex conjugate of  .
.
Select the complex conjugate of 
Tap to see back →
 can be restated in standard complex number form as
can be restated in standard complex number form as
 .
.
The complex conjugate of a complex number  is
is  , so the complex conjugate of
, so the complex conjugate of  is
is  , which is also equal to
, which is also equal to  . Therefore,
. Therefore,  itself is the complex conjugate of
itself is the complex conjugate of  .
.


The complex conjugate of a complex number 






Add:

Add:
Tap to see back →
When adding complex numbers, add the real parts and the imaginary parts separately to get another complex number in standard form.
Adding the real parts gives  , and adding the imaginary parts gives
, and adding the imaginary parts gives  .
.
When adding complex numbers, add the real parts and the imaginary parts separately to get another complex number in standard form.
Adding the real parts gives 

Subtract:

Subtract:
Tap to see back →
This is essentially the following expression after translation:

Now add the real parts together for a sum of  , and add the imaginary parts for a sum of
, and add the imaginary parts for a sum of  .
.
This is essentially the following expression after translation:
Now add the real parts together for a sum of 

Multiply:

Answer must be in standard form.
Multiply:
Answer must be in standard form.
Tap to see back →

The first step is to distribute which gives us:


which is in standard form.
The first step is to distribute which gives us:
which is in standard form.
Consider the following definitions of imaginary numbers:



Then, 
Consider the following definitions of imaginary numbers:
Then,
Tap to see back →
Divide: 
The answer must be in standard form.
Divide:
The answer must be in standard form.
Tap to see back →
Multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator which is  which results in
which results in

The numerator after simplification give us 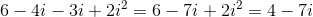
The denominator is equal to 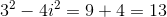
Hence, the final answer in standard form =

Multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator which is 
The numerator after simplification give us
The denominator is equal to
Hence, the final answer in standard form =
Divide: 
Answer must be in standard form.
Divide:
Answer must be in standard form.
Tap to see back →
Multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator which is  resulting in
resulting in

This is equal to 
Since  you can make that substitution of
you can make that substitution of  in place of
in place of  in both numerator and denominator, leaving:
in both numerator and denominator, leaving:

When you then cancel the negatives in both numerator and denominator (remember that  , simplifying each term), you're left with a denominator of
, simplifying each term), you're left with a denominator of  and a numerator of
and a numerator of  , which equals
, which equals  .
.
Multiply both the numerator and the denominator by the conjugate of the denominator which is 
This is equal to
Since 


When you then cancel the negatives in both numerator and denominator (remember that 



What is the absolute value of 
What is the absolute value of
Tap to see back →
The absolute value is a measure of the distance of a point from the origin. Using the pythagorean distance formula to calculate this distance.
The absolute value is a measure of the distance of a point from the origin. Using the pythagorean distance formula to calculate this distance.
Simplify the expression.

Simplify the expression.
Tap to see back →
Combine like terms. Treat  as if it were any other variable.
as if it were any other variable.


Substitute to eliminate  .
.


Simplify.

Combine like terms. Treat 
Substitute to eliminate 
Simplify.
What is the value of  ?
?
What is the value of 
Tap to see back →
Recall that the definition of imaginary numbers gives that  and thus that
and thus that  . Therefore, we can use Exponent Rules to write
. Therefore, we can use Exponent Rules to write 
Recall that the definition of imaginary numbers gives that 

What is the value of  ?
?
What is the value of 
Tap to see back →
When dealing with imaginary numbers, we multiply by foiling as we do with binomials. When we do this we get the expression below:

Since we know that  we get
we get  which gives us
which gives us  .
.
When dealing with imaginary numbers, we multiply by foiling as we do with binomials. When we do this we get the expression below:
Since we know that 


Evaluate: 
Evaluate:
Tap to see back →
Use the FOIL method to simplify. FOIL means to mulitply the first terms together, then multiply the outer terms together, then multiply the inner terms togethers, and lastly, mulitply the last terms together.

![=i[(1)(2)+(1)(-i)+(i)(2)+(i)(-i)]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/391457/gif.latex)



The imaginary  is equal to:
is equal to:

Write the terms for  .
.



Replace  with the appropiate values and simplify.
with the appropiate values and simplify.

Use the FOIL method to simplify. FOIL means to mulitply the first terms together, then multiply the outer terms together, then multiply the inner terms togethers, and lastly, mulitply the last terms together.
The imaginary 
Write the terms for 
Replace 
What is the value of  , if
, if  =
= ?
?
What is the value of 


Tap to see back →
We know that  . Therefore,
. Therefore,  . Thus, every exponent of
. Thus, every exponent of  that is a multiple of 4 will yield the value of
that is a multiple of 4 will yield the value of  . This makes
. This makes  . Since
. Since  , we know that
, we know that  .
.
We know that 






Tap to see back →

Combine like terms:

Distribute:

Combine like terms:


Combine like terms:
Distribute:
Combine like terms:
Tap to see back →
Multiply: 
Multiply:
Tap to see back →
Use FOIL to multiply the two binomials.
Recall that FOIL stands for Firsts, Outers, Inners, and Lasts.


Remember that 


Use FOIL to multiply the two binomials.
Recall that FOIL stands for Firsts, Outers, Inners, and Lasts.
Remember that
Rationalize the complex fraction: 
Rationalize the complex fraction:
Tap to see back →
To rationalize a complex fraction, multiply numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator.




To rationalize a complex fraction, multiply numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator.