Function Notation - Algebra 2
Card 0 of 196
Solve for  when
when  .
.
Solve for 

Tap to see back →
Plug 3 in for x:

Simplify:
= 
= 5
Plug 3 in for x:
Simplify:
=
= 5
What is
 ?
?


What is

Tap to see back →
To find the composition of two functions, substitute the second equation in to the first function.

Therefore,


and

Thus,
 .
.
To find the composition of two functions, substitute the second equation in to the first function.
Therefore,
and
Thus,

Solve the function for  . When
. When 
What does  equal when,
equal when, 

Solve the function for 
What does 
Tap to see back →
Plug 16 in for  .
. 
Add 9 to both sides. 
Take the square root of both sides.  =
=
Final answer is 

Plug 16 in for 
Add 9 to both sides.
Take the square root of both sides. 
Final answer is 
What is  of the following equation?
of the following equation?

What is 
Tap to see back →
To complete an equation with a 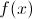 function, plug the number inside the parentheses into the equation for
function, plug the number inside the parentheses into the equation for  and solve algebraically.
and solve algebraically.
In this case the 
Square the 7 and multiply to get 
Add the numbers to get the answer  .
.
To complete an equation with a function, plug the number inside the parentheses into the equation for

In this case the
Square the 7 and multiply to get
Add the numbers to get the answer 
Given  , find
, find  .
.
Given 

Tap to see back →
Plug in a for x:

Next plug in (a + h) for x:

Therefore f(a+h) - f(a) =  .
.
Plug in a for x:
Next plug in (a + h) for x:
Therefore f(a+h) - f(a) = 
Tap to see back →
Tap to see back →
Use the function rule to find the  for the following function:
for the following function:

Use the function rule to find the 
Tap to see back →

Given  ,
,  , plug the value for x into the given equation and evaluate:
, plug the value for x into the given equation and evaluate:



Given 

Evaluate  if
if  and
and  .
.
Evaluate 


Tap to see back →

This expression is the same as saying "take the answer of  and plug it into
and plug it into  ."
."
First, we need to find  . We do this by plugging
. We do this by plugging  in for
in for  in
in  .
.


Now we take this answer and plug it into  .
.

We can find the value of  by replacing
by replacing  with
with  .
.


This is our final answer.
This expression is the same as saying "take the answer of 

First, we need to find 



Now we take this answer and plug it into 
We can find the value of 


This is our final answer.
Let  and
and  . What is
. What is  ?
?
Let 


Tap to see back →
THe notation  is a composite function, which means we put the inside function g(x) into the outside function f(x). Essentially, we look at the original expression for f(x) and replace each x with the value of g(x).
is a composite function, which means we put the inside function g(x) into the outside function f(x). Essentially, we look at the original expression for f(x) and replace each x with the value of g(x).
The original expression for f(x) is  . We will take each x and substitute in the value of g(x), which is 2x-1.
. We will take each x and substitute in the value of g(x), which is 2x-1.



We will now distribute the -2 to the 2x - 1.

We must FOIL the  term, because
term, because  .
.


Now we collect like terms. Combine the terms with just an x.

Combine constants.

The answer is  .
.
THe notation 
The original expression for f(x) is 
We will now distribute the -2 to the 2x - 1.
We must FOIL the 

Now we collect like terms. Combine the terms with just an x.
Combine constants.
The answer is 
Orange Taxi company charges passengers a $4.50 base fase, plus $0.10 per mile driven. Write a function to represent the cost of a cab ride, in terms of number of miles driven,  .
.
Orange Taxi company charges passengers a $4.50 base fase, plus $0.10 per mile driven. Write a function to represent the cost of a cab ride, in terms of number of miles driven, 
Tap to see back →
Total cost of the cab ride is going to equal the base fare ($4.50) plus an additional 10 cents per mile. This means the ride will always start off at $4.50. As the cab drives, the cost will increase by $0.10 each mile. This is represented as $0.10 times the number of miles. Therefore the total cost is:

Total cost of the cab ride is going to equal the base fare ($4.50) plus an additional 10 cents per mile. This means the ride will always start off at $4.50. As the cab drives, the cost will increase by $0.10 each mile. This is represented as $0.10 times the number of miles. Therefore the total cost is:
A small office building is to be built with  long walls
long walls  feet long and
feet long and  short walls
short walls  feet long each. The total length of the walls is to be
feet long each. The total length of the walls is to be  feet.
feet.
Write an equation for  in terms of
in terms of  .
.
A small office building is to be built with 




Write an equation for 

Tap to see back →
The pre-question text provides us with all of the information required to complete this problem.
We know that the total length of the walls is to be  ft.
ft.
We also know that we have a total of  walls and
walls and  walls.
walls.
With this, we can set up an equation and solve for  .
.
Our equation will be with sum of all the walls set equal to the total length of the wall...

Remeber, we want  in terms of
in terms of  , which means our equation should look like
, which means our equation should look like
 something
something
 Subtract
Subtract  on both sides
on both sides
 Divide by
Divide by  on both sides
on both sides
 Simplify
Simplify
 Answer!!!
Answer!!!
The pre-question text provides us with all of the information required to complete this problem.
We know that the total length of the walls is to be 
We also know that we have a total of 

With this, we can set up an equation and solve for 
Our equation will be with sum of all the walls set equal to the total length of the wall...
Remeber, we want 








A cable company charges a flat $29.99 activation fee, and an additional $12.99 per month for service. How would a function of the cost be represented in terms of months of service,  ?
?
A cable company charges a flat $29.99 activation fee, and an additional $12.99 per month for service. How would a function of the cost be represented in terms of months of service, 
Tap to see back →

The flat rate of 29.99 does not change depending on months of service. It is $29.99 no matter how long services are in use. The monthy fee is directly related to the number of months the services are in use.
The flat rate of 29.99 does not change depending on months of service. It is $29.99 no matter how long services are in use. The monthy fee is directly related to the number of months the services are in use.
What is the slope of the function  ?
?
What is the slope of the function 
Tap to see back →
The function is written in slope-intercept form, which means:

where:
 = slope
= slope
 = x value
= x value
 = y-intercept
= y-intercept
Therefore, the slope is 
The function is written in slope-intercept form, which means:
where:



Therefore, the slope is
If  , and
, and  , for which of the following
, for which of the following  value(s) will
value(s) will  be an odd number?
be an odd number?
If 



Tap to see back →
First, x needs to be plugged into g(x).
Then, the resulting solution needs to be substituted into f(x).
For example,
 .
.

Since 45 is an odd number, 7 is an x value that gives this result. Because both equations subtract an odd number to get the final result, only an odd number will result in an odd result therefore, none of the other options will give an odd result.
First, x needs to be plugged into g(x).
Then, the resulting solution needs to be substituted into f(x).
For example,

Since 45 is an odd number, 7 is an x value that gives this result. Because both equations subtract an odd number to get the final result, only an odd number will result in an odd result therefore, none of the other options will give an odd result.
Find  for the following function:
for the following function:

Find 
Tap to see back →
To evaluate  , we just plug in a
, we just plug in a  wherever we see an
wherever we see an  in the function, so our equation becomes
in the function, so our equation becomes

which is equal to

To evaluate 


which is equal to
Find  for the following function:
for the following function:

Find 
Tap to see back →
To find  , all we do is plug in
, all we do is plug in  wherever we see an
wherever we see an  in the function. We have to be sure we keep the parentheses. In this case, when we plug in
in the function. We have to be sure we keep the parentheses. In this case, when we plug in  , we get
, we get

Then, when we expand our binomial squared and distribute the  , we get
, we get

To find 



Then, when we expand our binomial squared and distribute the 
Evaluate the function for  .
.

Evaluate the function for 
Tap to see back →
To solve for the value of the function at  , simply plug in the value
, simply plug in the value  in place of every
in place of every  . By doing this, you will be left with the equation:
. By doing this, you will be left with the equation: .
.
Another way to go about the problem is first simplifying the expression so that like terms are collected, so  . Then to find
. Then to find  , simply plug in the value
, simply plug in the value  in place of every
in place of every  . By doing this, you will be left with the equation:
. By doing this, you will be left with the equation: .
.
To solve for the value of the function at 



Another way to go about the problem is first simplifying the expression so that like terms are collected, so 





If  , find
, find  .
.
If 

Tap to see back →
If  then
then  can be rewritten as
can be rewritten as  . Therefore,
. Therefore,  . Subtracting
. Subtracting  from both sides of the eqauation gives
from both sides of the eqauation gives  .
.
If 





Given  and
and  , find
, find  .
.


Given 


Tap to see back →
Given f(x) and g(x), find f(g(5))


This type of problem can look intimidating depending on how it is set up. What it is asking is for us to plug g(x) into f(x) everywhere we see an x, and then to plug in 5 everywhere we still have an x. It gets a little cumbersome if approached all at once:

This looks a bit unwieldy, but this problem can be approached easily by looking at it in layers.
First, find g(5)

 .
.
Next, plug that 15 into f(x).

So our answer is:

Given f(x) and g(x), find f(g(5))
This type of problem can look intimidating depending on how it is set up. What it is asking is for us to plug g(x) into f(x) everywhere we see an x, and then to plug in 5 everywhere we still have an x. It gets a little cumbersome if approached all at once:
This looks a bit unwieldy, but this problem can be approached easily by looking at it in layers.
First, find g(5)

Next, plug that 15 into f(x).
So our answer is:





