pH and POH of Strong Acids and Bases - AP Chemistry
Card 0 of 364
Which of the following is what determines the strength of an acid?
Which of the following is what determines the strength of an acid?
The Ka is the acid dissociation constant, and thus it is what determines how strong the acid is. Stronger acids dissociate to a greater extent and produce lower pH values.
The Ka is the acid dissociation constant, and thus it is what determines how strong the acid is. Stronger acids dissociate to a greater extent and produce lower pH values.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the defining characteristic of Bronsted-Lowry bases?
What is the defining characteristic of Bronsted-Lowry bases?
The definition of a Bronsted-Lowry base is a species that has the ability to gain, or accept a proton (H+). Dissociating in solution is part of the Arrhenius definition of acids and bases, and Lewis acid are electron pair acceptors.
The definition of a Bronsted-Lowry base is a species that has the ability to gain, or accept a proton (H+). Dissociating in solution is part of the Arrhenius definition of acids and bases, and Lewis acid are electron pair acceptors.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following can act as a Lewis base?
Which of the following can act as a Lewis base?
A Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. N atoms have a valence of 5, and in the NH2NH2 compound, it is only bonded to another N atom and 2 H, so it's only using 3 of its 5 valence electrons to form these bonds. Thus, each nitrogen has a pair of unbonded electrons and can act as a Lewis base.
A Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. N atoms have a valence of 5, and in the NH2NH2 compound, it is only bonded to another N atom and 2 H, so it's only using 3 of its 5 valence electrons to form these bonds. Thus, each nitrogen has a pair of unbonded electrons and can act as a Lewis base.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a Lewis base?
Which of the following is a Lewis base?
NH3 should be the clear correct choice, since it is the only one having a pair of electrons that are available. The rest of the answer choices are all Lewis acids.
NH3 should be the clear correct choice, since it is the only one having a pair of electrons that are available. The rest of the answer choices are all Lewis acids.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In the following equation, which is the conjugate base of HClO4?
HClO4 + H2O → ClO4– + H3O+
In the following equation, which is the conjugate base of HClO4?
HClO4 + H2O → ClO4– + H3O+
The conjugate base of an acid will be the same compound, short one H atom. ClO4– is the only one that meets this criterion.
The conjugate base of an acid will be the same compound, short one H atom. ClO4– is the only one that meets this criterion.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a Lewis base?
Which of the following is a Lewis base?
A Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. Only PH3 has a pair of nonbonding electrons and can act as a donor.
A Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. Only PH3 has a pair of nonbonding electrons and can act as a donor.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is the conjugate base of oxalic acid (H2C2O4)?
Which of the following is the conjugate base of oxalic acid (H2C2O4)?
The conjugate base has one less H atoms and one unit greater negative charge because of this. Thus, the correct answer is HC2O4–
The conjugate base has one less H atoms and one unit greater negative charge because of this. Thus, the correct answer is HC2O4–
Compare your answer with the correct one above
BCl3 is a .
BCl3 is a .
A Lewis acid is a species that can accept an electron pair. In the BCl3 molecule, B does not have a complete octet (3 covalent bonds, thus 6 electrons around it rather than 8). Thus, it can accept another electron pair, making it a Lewis acid.
A Lewis acid is a species that can accept an electron pair. In the BCl3 molecule, B does not have a complete octet (3 covalent bonds, thus 6 electrons around it rather than 8). Thus, it can accept another electron pair, making it a Lewis acid.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In the following reaction, which is the conjugate acid?
HCO3– + HCl → H2CO3 + Cl–
In the following reaction, which is the conjugate acid?
HCO3– + HCl → H2CO3 + Cl–
Conjugate acid has one more H+ than the compound with which it is being compared. Thus, H2CO3 is the conjugate acid of HCO3–.
Conjugate acid has one more H+ than the compound with which it is being compared. Thus, H2CO3 is the conjugate acid of HCO3–.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a strong acid?
Which of the following is a strong acid?
This question is simply testing your memorization of strong and weak acids. Of the list, you should recognize that nitric acid is the only strong acid, and the rest of the choices are weak.
This question is simply testing your memorization of strong and weak acids. Of the list, you should recognize that nitric acid is the only strong acid, and the rest of the choices are weak.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following solutions will have a pH greater than 7?
Which of the following solutions will have a pH greater than 7?
HCN, HCl, CH3COOH, and NH4Cl are all acids (NH4+ is the ammonium ion). That only leaves KCN as the correct answer.
HCN, HCl, CH3COOH, and NH4Cl are all acids (NH4+ is the ammonium ion). That only leaves KCN as the correct answer.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Would H2SO4 or HNO3 produce a more acidic solution?
Would H2SO4 or HNO3 produce a more acidic solution?
Both are strong acids, but H2SO4 is bivalent, realeasing 2 protons for each molecule dissolved in solution. Further, a more acidic solution would have a lower pKa.
Both are strong acids, but H2SO4 is bivalent, realeasing 2 protons for each molecule dissolved in solution. Further, a more acidic solution would have a lower pKa.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Under which classification(s) of acid does  fall?
fall?
Under which classification(s) of acid does 
Every Lewis acid is also a Brønsted-Lowry acid, and every Brønsted-Lowry acid is an Arrhenius acid; thus, H2SO4 is all three, since it is an Arrhenius acid: (it dissolves in water to produce a proton). Sulfuric acid is also considered a strong acid, as it full dissociates in water.
Every Lewis acid is also a Brønsted-Lowry acid, and every Brønsted-Lowry acid is an Arrhenius acid; thus, H2SO4 is all three, since it is an Arrhenius acid: (it dissolves in water to produce a proton). Sulfuric acid is also considered a strong acid, as it full dissociates in water.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a pairing between an acid and its conjugate base?
Which of the following is a pairing between an acid and its conjugate base?
The conjugate base of an acid is the same formula, minus one proton. The only option that fits this description is the one that includes the hydronium ion (H3O+) and water (H2O).
The conjugate base of an acid is the same formula, minus one proton. The only option that fits this description is the one that includes the hydronium ion (H3O+) and water (H2O).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following species will not be present in an aqueous solution of  ?
?
Which of the following species will not be present in an aqueous solution of 
The hydroxide ion (OH–) is a strong base and therefore would not be present in an acidic solution. Protons, the hydronium ion, and water will all be present in relatively large amounts within the solution.
The hydroxide ion (OH–) is a strong base and therefore would not be present in an acidic solution. Protons, the hydronium ion, and water will all be present in relatively large amounts within the solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not true of a neutralization reaction?
Which of the following is not true of a neutralization reaction?
The PRODUCTS of a neutralization reactions are salt and water, not the reactants. The rest of the options all correctly pertain to neutralization reactions.
The PRODUCTS of a neutralization reactions are salt and water, not the reactants. The rest of the options all correctly pertain to neutralization reactions.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds is a Lewis acid: HCl, AlCl_3, NH_3, H_2SO_4?
Which of the following compounds is a Lewis acid: HCl, AlCl_3, NH_3, H_2SO_4?
A Lewis acid is a 2-electron acceptor, and a Lewis base is a 2-electron donor.
HCl, while it is acidic, cannot accept two electrons, so it is not a Lewis acid.
AlCl_3 can accept two electrons, so it is a Lewis acid.
NH_3 is a Lewis base.
H_2SO_4, like hydrochloric acid, is acidic, but cannot accept two electrons, so it is not a Lewis acid.
A Lewis acid is a 2-electron acceptor, and a Lewis base is a 2-electron donor.
HCl, while it is acidic, cannot accept two electrons, so it is not a Lewis acid.
AlCl_3 can accept two electrons, so it is a Lewis acid.
NH_3 is a Lewis base.
H_2SO_4, like hydrochloric acid, is acidic, but cannot accept two electrons, so it is not a Lewis acid.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider the following chemical reaction.

What phenomena is this responsible for?
Consider the following chemical reaction.
What phenomena is this responsible for?

The above reaction describes the reaction that occurs when carbon dioxide dissolves in water and reacts to form carbonic acid, which is responsible for acid rain.
The phenomenon seen by dry ice is simply the sublimation of carbon dioxide. Acids and bases do not usually react in a violent fashion. The reaction between baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and vinegar (acetic acid) is given below. The production of carbon dioxide gas is responsible for the bubbles seen in this reaction.
The above reaction describes the reaction that occurs when carbon dioxide dissolves in water and reacts to form carbonic acid, which is responsible for acid rain.
The phenomenon seen by dry ice is simply the sublimation of carbon dioxide. Acids and bases do not usually react in a violent fashion. The reaction between baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and vinegar (acetic acid) is given below. The production of carbon dioxide gas is responsible for the bubbles seen in this reaction.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following salts will result in an acidic solution?
Which of the following salts will result in an acidic solution?
All of the listed salts will dissolve into ions when in water. When the ions are in solution, they can act as acids or bases by donating or accepting protons. Chloride, bromide, and iodide ions are all conjugate bases of strong acids, so they will not accept protons. Sodium and potassium ions are the conjugate acids of strong bases, which dissociate completely, so they will not accept hydroxide ions.
Ammonium is the conjugate acid of ammonia, a weak base. The ammonium ion can donate a proton to the solution. This will make the solution slightly acidic. As a result, ammonium bromide is a salt that will make an acidic solution.
All of the listed salts will dissolve into ions when in water. When the ions are in solution, they can act as acids or bases by donating or accepting protons. Chloride, bromide, and iodide ions are all conjugate bases of strong acids, so they will not accept protons. Sodium and potassium ions are the conjugate acids of strong bases, which dissociate completely, so they will not accept hydroxide ions.
Ammonium is the conjugate acid of ammonia, a weak base. The ammonium ion can donate a proton to the solution. This will make the solution slightly acidic. As a result, ammonium bromide is a salt that will make an acidic solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A 1M solution of a monoprotic acid has a pH of 4.6. What is the 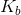 value for the conjugate base of the acid?
value for the conjugate base of the acid?
A 1M solution of a monoprotic acid has a pH of 4.6. What is the 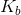
In order to find the base dissociation constant for the conjugate base, we can start by finding the acid dissociation constant for the acid. Since a 1M solution of the acid has a pH of 4.6, we can find the proton concentration of the solution.
![pH=-\log[H^+]\rightarrow [H^$+]=10^{-pH}$](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/121717/gif.latex)
![\small $[H^{+}$] = $10^{-4.6}$ = $2.51*10^{-5}$](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94835/gif.latex)
Since the acid is monoprotic, we can set the following equilibrium expression equal to its acid dissociation constant.
![\small $K_{a}$ = $$\frac{[H^{+}$$$][A^{-}$]}{[HA]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/121718/gif.latex)
We can see that, since the acid is monoprotic, the concntration of protons will be equal to the concentration of the acid anion. The final concentration of the acid molecule will be equal to the initial concentration, minus the amount of protons formed. Using these values, we can solve for the equilibrium constant for the acid.
![K_a= $$\frac{[2.51*10^{-5}$$$]^{2}$$}{[1-2.51*10^{-5}$]} = $6.31*10^{-10}$](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94836/gif.latex)
Now that we have the acid dissociation constant, we can find the conjugate base's dissociation constant by setting the product of the two values equal to the autoionization of water.

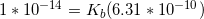

In order to find the base dissociation constant for the conjugate base, we can start by finding the acid dissociation constant for the acid. Since a 1M solution of the acid has a pH of 4.6, we can find the proton concentration of the solution.
Since the acid is monoprotic, we can set the following equilibrium expression equal to its acid dissociation constant.
We can see that, since the acid is monoprotic, the concntration of protons will be equal to the concentration of the acid anion. The final concentration of the acid molecule will be equal to the initial concentration, minus the amount of protons formed. Using these values, we can solve for the equilibrium constant for the acid.
Now that we have the acid dissociation constant, we can find the conjugate base's dissociation constant by setting the product of the two values equal to the autoionization of water.
Compare your answer with the correct one above