Biochemistry and Metabolism - MCAT Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
Card 0 of 472
During cellular respiration, where is NADH produced?
During cellular respiration, where is NADH produced?
NADH is produced during glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm. NADH is also produced during the Krebs cycle, which occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. The protons generated in the production of NADH are later used in the intermembrane space to power ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation.
NADH is produced during glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm. NADH is also produced during the Krebs cycle, which occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. The protons generated in the production of NADH are later used in the intermembrane space to power ATP synthase during oxidative phosphorylation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the purpose of the formation of lactic acid during anaerobic respiration?
What is the purpose of the formation of lactic acid during anaerobic respiration?
Cells need a constant supply of NAD+ to accept electrons during glycolysis in order to produce pyruvate from glucose.
Cells need a constant supply of NAD+ to accept electrons during glycolysis in order to produce pyruvate from glucose.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which process can occur under anaerobic conditions?
Which process can occur under anaerobic conditions?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol and does not require oxygen. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and Kreb's cycle require oxygen indirectly, while the electron transport chain and oxydative phosphorylation require oxygen directly. After glycolysis produces pyruvate, either aerobic respiration or anaerobic respiration can proceed depending on the availability of oxygen.
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol and does not require oxygen. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) and Kreb's cycle require oxygen indirectly, while the electron transport chain and oxydative phosphorylation require oxygen directly. After glycolysis produces pyruvate, either aerobic respiration or anaerobic respiration can proceed depending on the availability of oxygen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which statement is FALSE when comparing aerobic to anaerobic respiration?
Which statement is FALSE when comparing aerobic to anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration creates the byproduct lactic acid. Accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles due to lack of oxygen results in the pain we experience during exercise. Remember that aerobic respiration creates 36 ATP molecules per glucose, while anaerobic repiration forms only 2 ATP molecules per glucose. Since both processes begin with glycolysis, pyruvate is still generated.
Note that while lactic acid is responsible for the "burn" in muscles during exercise, other agents are responsible for muscle soreness after exercise.
Anaerobic respiration creates the byproduct lactic acid. Accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles due to lack of oxygen results in the pain we experience during exercise. Remember that aerobic respiration creates 36 ATP molecules per glucose, while anaerobic repiration forms only 2 ATP molecules per glucose. Since both processes begin with glycolysis, pyruvate is still generated.
Note that while lactic acid is responsible for the "burn" in muscles during exercise, other agents are responsible for muscle soreness after exercise.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
While running a marathon, an individual feels pain and a burning sensation in her legs. One reason for this is the conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid which the body does in order to .
While running a marathon, an individual feels pain and a burning sensation in her legs. One reason for this is the conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid which the body does in order to .
In the absence of available oxygen, the body conducts metabolism anaerobically in a process known as fermentation. During strenuous exercise, like running a marathon, the body needs to generate ATP at a rate faster than oxygen is becoming available.
To combat this issue, the body converts pyruvate and NADH, generated in glycolysis, into lactic acid and NAD+, respectively. This regenerated NAD+ can participate in further glycolysis to generate more ATP, even in the absence of oxygen. Oxygen only becomes a necessary reactant in the electron transport chain; thus, glycolysis can continue to generate limited amounts of ATP in an anaerobic environment as long as NAD+ is present.
In the absence of available oxygen, the body conducts metabolism anaerobically in a process known as fermentation. During strenuous exercise, like running a marathon, the body needs to generate ATP at a rate faster than oxygen is becoming available.
To combat this issue, the body converts pyruvate and NADH, generated in glycolysis, into lactic acid and NAD+, respectively. This regenerated NAD+ can participate in further glycolysis to generate more ATP, even in the absence of oxygen. Oxygen only becomes a necessary reactant in the electron transport chain; thus, glycolysis can continue to generate limited amounts of ATP in an anaerobic environment as long as NAD+ is present.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following products cannot be directly formed from pyruvate?
Which of the following products cannot be directly formed from pyruvate?
Pyruvate can be decarboxylated to make acetyl-CoA. This is the process that initiates the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate can also undergo fermentation, and be reduced to either lactic acid or acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde can then be reduced to ethanol, however, pyruvate cannot directly be converted to ethanol.
Pyruvate can be decarboxylated to make acetyl-CoA. This is the process that initiates the citric acid cycle. Pyruvate can also undergo fermentation, and be reduced to either lactic acid or acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde can then be reduced to ethanol, however, pyruvate cannot directly be converted to ethanol.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the purpose of fermentation?
What is the purpose of fermentation?
Fermentation occurs in the absence of oxygen, and reduces pyruvate to the end product of either ethanol or lactic acid. Since pyruvate is being reduced, NADH is oxidized to NAD+, which is needed for the initial glycolysis reaction to produce pyruvate. During anaerobic respiration, glycolysis is still able to function, but only if NAD+ is available; thus, fermentation allows the regeneration of NAD+ in order for glycolysis to proceed in the absence of oxygen.
Fermentation occurs in the absence of oxygen, and reduces pyruvate to the end product of either ethanol or lactic acid. Since pyruvate is being reduced, NADH is oxidized to NAD+, which is needed for the initial glycolysis reaction to produce pyruvate. During anaerobic respiration, glycolysis is still able to function, but only if NAD+ is available; thus, fermentation allows the regeneration of NAD+ in order for glycolysis to proceed in the absence of oxygen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which choice accurately states the amount of ATP produced from a single glucose molecule in an anaerobic environment and in an aerobic environment, respectively?
Which choice accurately states the amount of ATP produced from a single glucose molecule in an anaerobic environment and in an aerobic environment, respectively?
In an anaerobic environment, two net ATP are produced from glycolysis. Since glycolysis requires an investment of two ATP and produces four ATP, it has a total net yield of two ATP. In an aerobic environment, however, the cell performs glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These processes together yield a net of 36 ATP.
In an anaerobic environment, two net ATP are produced from glycolysis. Since glycolysis requires an investment of two ATP and produces four ATP, it has a total net yield of two ATP. In an aerobic environment, however, the cell performs glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These processes together yield a net of 36 ATP.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
How many molecules of ATP would be produced and available for use if four molecules of glucose were used during anaerobic respiration?
How many molecules of ATP would be produced and available for use if four molecules of glucose were used during anaerobic respiration?
Two net molecules of ATP are produced via anaerobic cellular respiration.
Two net molecules of ATP are produced via anaerobic cellular respiration.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the net ATP production if 4 glucose molecules are oxidized in anaerobic conditions?
What is the net ATP production if 4 glucose molecules are oxidized in anaerobic conditions?
During anaerobic conditions only glycolysis occurs. Glycolysis alone produces 4 ATP per glucose, but requires an input of 2 ATP per glucose. Thus, 2 ATP per glucose are yielded through glycolysis.
During anaerobic conditions only glycolysis occurs. Glycolysis alone produces 4 ATP per glucose, but requires an input of 2 ATP per glucose. Thus, 2 ATP per glucose are yielded through glycolysis.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The drug, DNP, destroys the H+ gradient that forms in the electron transport chain. What is the most likely consequence?
The drug, DNP, destroys the H+ gradient that forms in the electron transport chain. What is the most likely consequence?
If the proton gradient of the electron transport chain were to be destroyed, the cell would need to perform cellular respiration without an electron transport chain. The only option would be to move to anaerobic respiration, which requires fermentation.
If the proton gradient of the electron transport chain were to be destroyed, the cell would need to perform cellular respiration without an electron transport chain. The only option would be to move to anaerobic respiration, which requires fermentation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Given a healthy individual with a normal metabolic rate, which of the following compounds is the most energy rich?
Given a healthy individual with a normal metabolic rate, which of the following compounds is the most energy rich?
This question is asking about ATP production during cellular respiration. During oxidative phosphorylation (the electron transport chain), each 1 ATP is produced for each GTP, 2 ATP are produced for each FADH2, and 3 ATP are produced for each NADH.
This question is asking about ATP production during cellular respiration. During oxidative phosphorylation (the electron transport chain), each 1 ATP is produced for each GTP, 2 ATP are produced for each FADH2, and 3 ATP are produced for each NADH.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A person is born with a mutation that causes their cells to not have the ability to produce the NADH dehydrogenase complex, the complex that allows the electron transport chain to make ATP from NADH. Will this patient be able to produce any enery at all from the ETC?
A person is born with a mutation that causes their cells to not have the ability to produce the NADH dehydrogenase complex, the complex that allows the electron transport chain to make ATP from NADH. Will this patient be able to produce any enery at all from the ETC?
FADH2 enters the ETC at the succinate-Q oxidoreductase complex. While this doesn't generate as much energy as NADH will because the electrons travel a shorter distance, there are still 2 ATP molecules made for each FADH2.
FADH2 enters the ETC at the succinate-Q oxidoreductase complex. While this doesn't generate as much energy as NADH will because the electrons travel a shorter distance, there are still 2 ATP molecules made for each FADH2.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
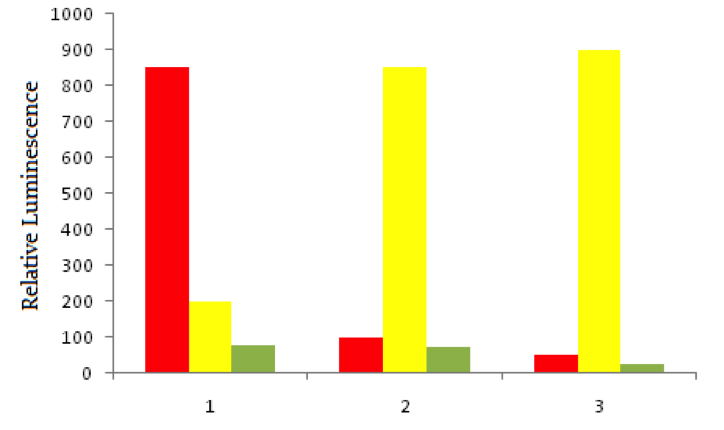
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.
Cancer cells require large amounts of energy in the form of ATP. Which of the following processes results in the greatest production of ATP?
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.

Cancer cells require large amounts of energy in the form of ATP. Which of the following processes results in the greatest production of ATP?
Oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria is the major contributor to the total ATP pool in most eukaryotic cells. Keep in mind that it is oxidative phosphorylation in concert with the proton gradient that drives the electron transport chain.
Oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria is the major contributor to the total ATP pool in most eukaryotic cells. Keep in mind that it is oxidative phosphorylation in concert with the proton gradient that drives the electron transport chain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.

A new treatment for bladder cancer is developed that targets energy production in malignant cells. Which of the following potential target sites would directly involve the synthesis of most of the ATP in a cell?
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.

A new treatment for bladder cancer is developed that targets energy production in malignant cells. Which of the following potential target sites would directly involve the synthesis of most of the ATP in a cell?
ATP synthase is housed on the inner mitochondrial membrane, and is the main ATP production agent in oxidative phosphorylation. It provides a channel for protons to enter the matrix from the intermembrane space, and in so doing, drives ATP production.
ATP synthase is housed on the inner mitochondrial membrane, and is the main ATP production agent in oxidative phosphorylation. It provides a channel for protons to enter the matrix from the intermembrane space, and in so doing, drives ATP production.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What phase of cellular respiration has the highest ATP yield?
What phase of cellular respiration has the highest ATP yield?
Oxidative phosphorylation, which traps energy in a high-energy phosphate bond and uses an electron gradient and ATP synthase to create ATP, yields the most ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is linked with the electron transport chain.
Glycolysis only gives a net of two ATP per glucose, and the Krebs cycle gives two GTP for every turn of the cycle. Gluconeogenesis is not a part of cellular respiration, and fermentation is very low-yield since it occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Oxidative phosphorylation, which traps energy in a high-energy phosphate bond and uses an electron gradient and ATP synthase to create ATP, yields the most ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is linked with the electron transport chain.
Glycolysis only gives a net of two ATP per glucose, and the Krebs cycle gives two GTP for every turn of the cycle. Gluconeogenesis is not a part of cellular respiration, and fermentation is very low-yield since it occurs in the absence of oxygen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Why is oxygen necessary in aerobic cellular respiration?
Why is oxygen necessary in aerobic cellular respiration?
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, which results in the production of water. Glycolysis does not require oxygen, and can be done in anaerobic environments. NADH is the molecule which is oxidized in order to establish the proton gradient. Finally, oxygen is not needed to create oxaloacetic acid is the Kreb's cycle, as it is regenerated after each turn of the cycle.
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, which results in the production of water. Glycolysis does not require oxygen, and can be done in anaerobic environments. NADH is the molecule which is oxidized in order to establish the proton gradient. Finally, oxygen is not needed to create oxaloacetic acid is the Kreb's cycle, as it is regenerated after each turn of the cycle.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Imagine that a toxin is introduced to the body and inhibits the establishment of the proton gradient in the intermembrane space. What would you predict would be the result?
Imagine that a toxin is introduced to the body and inhibits the establishment of the proton gradient in the intermembrane space. What would you predict would be the result?
ATP synthase is dependent on a proton gradient in the intermembrane space in order to produce ATP. As a result, the toxin will make it inactive. Oxidative phosphorylation would be inhibited in this case, as opposed to substrate-level phosphorylation.
Pyruvate is a product of glycolysis, and would not be affected by the toxin. NADH is key in the establishment of the proton gradient, so we would expect that it would be unable to be oxidized due to the toxin. Protons produced in the conversion of NADH to NAD+ (+H+) establish the proton gradient. If the gradient is absent, NADH is likely not be oxidized.
ATP synthase is dependent on a proton gradient in the intermembrane space in order to produce ATP. As a result, the toxin will make it inactive. Oxidative phosphorylation would be inhibited in this case, as opposed to substrate-level phosphorylation.
Pyruvate is a product of glycolysis, and would not be affected by the toxin. NADH is key in the establishment of the proton gradient, so we would expect that it would be unable to be oxidized due to the toxin. Protons produced in the conversion of NADH to NAD+ (+H+) establish the proton gradient. If the gradient is absent, NADH is likely not be oxidized.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Most scientists subscribe to the theory of endosymbiosis to explain the presence of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. According to the theory of endosymbiosis, early pre-eukaryotic cells phagocytosed free living prokaryotes, but failed to digest them. As a result, these prokaryotes remained in residence in the pre-eukaryotes, and continued to generate energy. The host cells were able to use this energy to gain a selective advantage over their competitors, and eventually the energy-producing prokaryotes became mitochondria.
In many ways, mitochondria are different from other cellular organelles, and these differences puzzled scientists for many years. The theory of endosymbiosis concisely explains a number of these observations about mitochondria. Perhaps most of all, the theory explains why aerobic metabolism is entirely limited to this one organelle, while other kinds of metabolism are more distributed in the cellular cytosol.
One of the main arguments in favor of the theory of endosymbiosis is that mitochondria have their own genome. Which of the following cellular structures is most likely to be coded for only by mitochondrial DNA?
Most scientists subscribe to the theory of endosymbiosis to explain the presence of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. According to the theory of endosymbiosis, early pre-eukaryotic cells phagocytosed free living prokaryotes, but failed to digest them. As a result, these prokaryotes remained in residence in the pre-eukaryotes, and continued to generate energy. The host cells were able to use this energy to gain a selective advantage over their competitors, and eventually the energy-producing prokaryotes became mitochondria.
In many ways, mitochondria are different from other cellular organelles, and these differences puzzled scientists for many years. The theory of endosymbiosis concisely explains a number of these observations about mitochondria. Perhaps most of all, the theory explains why aerobic metabolism is entirely limited to this one organelle, while other kinds of metabolism are more distributed in the cellular cytosol.
One of the main arguments in favor of the theory of endosymbiosis is that mitochondria have their own genome. Which of the following cellular structures is most likely to be coded for only by mitochondrial DNA?
Electron transport chain (ETC) proteins are encoded by the the mitochondrial DNA. This makes sense, as we find ETC proteins only in the mitochondrial membrane (remember, as the passage states, aerobic metabolism is limited to the mitochondria).
It may be tempting to select glycolytic enzymes, as the free living predecessors to mitochondria presumably underwent glycolysis; however, these genes have been lost as the symbiosis matured and glycolysis was localized to the cellular cytosol.
Electron transport chain (ETC) proteins are encoded by the the mitochondrial DNA. This makes sense, as we find ETC proteins only in the mitochondrial membrane (remember, as the passage states, aerobic metabolism is limited to the mitochondria).
It may be tempting to select glycolytic enzymes, as the free living predecessors to mitochondria presumably underwent glycolysis; however, these genes have been lost as the symbiosis matured and glycolysis was localized to the cellular cytosol.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Most scientists subscribe to the theory of endosymbiosis to explain the presence of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. According to the theory of endosymbiosis, early pre-eukaryotic cells phagocytosed free living prokaryotes, but failed to digest them. As a result, these prokaryotes remained in residence in the pre-eukaryotes, and continued to generate energy. The host cells were able to use this energy to gain a selective advantage over their competitors, and eventually the energy-producing prokaryotes became mitochondria.
In many ways, mitochondria are different from other cellular organelles, and these differences puzzled scientists for many years. The theory of endosymbiosis concisely explains a number of these observations about mitochondria. Perhaps most of all, the theory explains why aerobic metabolism is entirely limited to this one organelle, while other kinds of metabolism are more distributed in the cellular cytosol.
With regard to the energy production by the mitochondria discussed in the passage, what is the main factor driving ATP production at the terminal step of aerobic metabolism?
Most scientists subscribe to the theory of endosymbiosis to explain the presence of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. According to the theory of endosymbiosis, early pre-eukaryotic cells phagocytosed free living prokaryotes, but failed to digest them. As a result, these prokaryotes remained in residence in the pre-eukaryotes, and continued to generate energy. The host cells were able to use this energy to gain a selective advantage over their competitors, and eventually the energy-producing prokaryotes became mitochondria.
In many ways, mitochondria are different from other cellular organelles, and these differences puzzled scientists for many years. The theory of endosymbiosis concisely explains a number of these observations about mitochondria. Perhaps most of all, the theory explains why aerobic metabolism is entirely limited to this one organelle, while other kinds of metabolism are more distributed in the cellular cytosol.
With regard to the energy production by the mitochondria discussed in the passage, what is the main factor driving ATP production at the terminal step of aerobic metabolism?
The final step in aerobic metabolism is the capture of the stored energy of protons existing in the intermembrane space. The electrochemical gradient in the intermembrane space forces protons through ATP synthase, phosphorylating ADP.
Glucose is converted to pyruvate during glycolysis, and to lactate during anaerobic respiration.
The final step in aerobic metabolism is the capture of the stored energy of protons existing in the intermembrane space. The electrochemical gradient in the intermembrane space forces protons through ATP synthase, phosphorylating ADP.
Glucose is converted to pyruvate during glycolysis, and to lactate during anaerobic respiration.
Compare your answer with the correct one above