Specific Reactions and Named Reactions - Organic Chemistry
Card 0 of 260
Which substrate, when subjected to ozonolysis followed by treatment with dimethyl sulfide, would give only one hydrocarbon product?
Which substrate, when subjected to ozonolysis followed by treatment with dimethyl sulfide, would give only one hydrocarbon product?
Ozonolysis is essentially used to cleave a compound at the location of a double bond. For the result to be a single product, the cleavage must occur at a point of symmetry.
4-octene, a symmetrical alkene, would give two equivalents of butanal upon ozonolysis. All of the other compounds are unsymmetrical and would give at least two different non-identical products.
Ozonolysis is essentially used to cleave a compound at the location of a double bond. For the result to be a single product, the cleavage must occur at a point of symmetry.
4-octene, a symmetrical alkene, would give two equivalents of butanal upon ozonolysis. All of the other compounds are unsymmetrical and would give at least two different non-identical products.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


First step: esterification
Second step: reduction
Third step: neutralization
Fourth step: oxidation to aldehyde
Fifth step: alkene metathesis
First step: esterification
Second step: reduction
Third step: neutralization
Fourth step: oxidation to aldehyde
Fifth step: alkene metathesis
Compare your answer with the correct one above

Why does the reaction above require the use of Ag2O?

Why does the reaction above require the use of Ag2O?
The Ag2O oxidizes the alcohol to form the alkoxide ion. The Ag2O is a reducing agent, and it oxidizes the alcohol because the alcohol loses a proton. Ag2O is a strong base, meaning it will accept protons readily. The given reaction is an example of Williamson ether synthesis. This reaction occurs via an SN2 pathway.
The Ag2O oxidizes the alcohol to form the alkoxide ion. The Ag2O is a reducing agent, and it oxidizes the alcohol because the alcohol loses a proton. Ag2O is a strong base, meaning it will accept protons readily. The given reaction is an example of Williamson ether synthesis. This reaction occurs via an SN2 pathway.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the product of the given reaction?

What is the product of the given reaction?
This is a classic Diels-Alder reaction and it consists of a diene (cyclopentadiene) and a dienophile (ethene). The bicyclic structure forms if the electrons are moved in a circular fashion.
This is a classic Diels-Alder reaction and it consists of a diene (cyclopentadiene) and a dienophile (ethene). The bicyclic structure forms if the electrons are moved in a circular fashion.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What reaction forms a substituted cyclohexene system?
What reaction forms a substituted cyclohexene system?
The Diels-Alder reaction converts a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene into a six-membered ring containing cyclohexene (a substituted cyclohexene system). In Hoffmann elimination, tetra-alkyl ammonium salts undergo elimination to form the least substituted alkene. The Wittig reaction uses phosphorus ylides, aldehydes, or ketones to form an alkene and a triphenylphosphine oxide. Lastly, Gabriel synthesis forms primary amines via the reaction of a phthalimide with an alkyl halide, followed by cleavage with hydrazine.
The Diels-Alder reaction converts a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene into a six-membered ring containing cyclohexene (a substituted cyclohexene system). In Hoffmann elimination, tetra-alkyl ammonium salts undergo elimination to form the least substituted alkene. The Wittig reaction uses phosphorus ylides, aldehydes, or ketones to form an alkene and a triphenylphosphine oxide. Lastly, Gabriel synthesis forms primary amines via the reaction of a phthalimide with an alkyl halide, followed by cleavage with hydrazine.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
When the following reaction is carried out, what kind of product is formed:

Note: When an organic reaction employs heat, it is often shown as a delta over the reaction arrow.
When the following reaction is carried out, what kind of product is formed:

Note: When an organic reaction employs heat, it is often shown as a delta over the reaction arrow.
This is a Diels-Alder reaction; these reactions happen between a nucleophilic diene, shown in blue below, and an electrophilic dienophile, in green. Diels-Alder reactions install a set of bonds that connect each external carbon of the diene system to an alkene carbon in the dienophile system to create a new six-membered ring. All remaining structure of the two reactants are retained, including the six- and five-membered rings below. The red bonds are the newly installed bonds.

This is a Diels-Alder reaction; these reactions happen between a nucleophilic diene, shown in blue below, and an electrophilic dienophile, in green. Diels-Alder reactions install a set of bonds that connect each external carbon of the diene system to an alkene carbon in the dienophile system to create a new six-membered ring. All remaining structure of the two reactants are retained, including the six- and five-membered rings below. The red bonds are the newly installed bonds.

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the product of the reaction between 1,3-dibutene and bromoethene?
What is the product of the reaction between 1,3-dibutene and bromoethene?
The electrons from one of the double bonds on the 1,3-dibutene create a new single bond. The other new single bond is created from the electrons in the double bond of the other reactant. These two new single bonds join the reactants to create a cyclic product.
The electrons from the other double bond in the 1,3-dibutene move between the carbon 2 and 3. Thus, the final product is a 6-carbon cycloalkene with a halogen substituent.
The electrons from one of the double bonds on the 1,3-dibutene create a new single bond. The other new single bond is created from the electrons in the double bond of the other reactant. These two new single bonds join the reactants to create a cyclic product.
The electrons from the other double bond in the 1,3-dibutene move between the carbon 2 and 3. Thus, the final product is a 6-carbon cycloalkene with a halogen substituent.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What reagent(s) is/are needed to drive the given reaction?
What reagent(s) is/are needed to drive the given reaction?
This is a standard Diels-Alder reaction. Diels-Alder reactions are driven solely by adding heat to the reagents. By looking at the reagents and the product, we can tell that this is a Diels-Alder reaction. For Diels-Alder, we need a cis-diene and an alkene as reactants. When these reactants are stimulated by heat, they form a cyclohexene product.
This is a standard Diels-Alder reaction. Diels-Alder reactions are driven solely by adding heat to the reagents. By looking at the reagents and the product, we can tell that this is a Diels-Alder reaction. For Diels-Alder, we need a cis-diene and an alkene as reactants. When these reactants are stimulated by heat, they form a cyclohexene product.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the product of the given reaction?

What is the product of the given reaction?

Diels-Alder reactions create cyclohexene rings (eliminate III, IV, and V), and starting dienophile is trans (E conformation), so product is E (Eliminate I).
Diels-Alder reactions create cyclohexene rings (eliminate III, IV, and V), and starting dienophile is trans (E conformation), so product is E (Eliminate I).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Cyclohexene undergoes hydrobromination.
Which of these is a possible product?
Cyclohexene undergoes hydrobromination.
Which of these is a possible product?
Only bromocyclohexane is created because there is only one bromine group that bonds with one of the carbons, while the other carbon is bonded with hydrogen group.
Only bromocyclohexane is created because there is only one bromine group that bonds with one of the carbons, while the other carbon is bonded with hydrogen group.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Ozonolysis of an alkyne results in the products 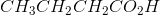 and
and  . What is the IUPAC name of the original compound?
. What is the IUPAC name of the original compound?
Ozonolysis of an alkyne results in the products 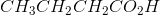

Ozonolysis of the alkyne breaks the alkyne at the triple bond. The carbons that were in the triple bond become the carbons of either a ketone or a carboxylic acid depending on if they are terminal or not.
Working backwards, one can take the products and remove their oxygens. Then, the carbons from which the oxygens were removed should be triple bonded. The initial compound has seven carbons in its longest chain. Counting from the side closest to the bond, C2 has two methyl groups bound to it. The triple bond runs across C3 and C4. Thus the answer is 2,2-dimethyl-3-heptyne.
Ozonolysis of the alkyne breaks the alkyne at the triple bond. The carbons that were in the triple bond become the carbons of either a ketone or a carboxylic acid depending on if they are terminal or not.
Working backwards, one can take the products and remove their oxygens. Then, the carbons from which the oxygens were removed should be triple bonded. The initial compound has seven carbons in its longest chain. Counting from the side closest to the bond, C2 has two methyl groups bound to it. The triple bond runs across C3 and C4. Thus the answer is 2,2-dimethyl-3-heptyne.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
An organic chemist reacts one mole of 4-octene with excess  . What is the final product?
. What is the final product?
An organic chemist reacts one mole of 4-octene with excess 
These are standard conditions for an ozonolysis reaction. For an ozonolysis reaction to take place, all we need is an alkene and ozone. The ozone essentially cuts the alkene in half and adds a carbonyl group to each half of the carbon chain.
These are standard conditions for an ozonolysis reaction. For an ozonolysis reaction to take place, all we need is an alkene and ozone. The ozone essentially cuts the alkene in half and adds a carbonyl group to each half of the carbon chain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What reagent(s) will successfully complete the synthesis reaction shown above?

What reagent(s) will successfully complete the synthesis reaction shown above?
This is an example of a Grignard reagent reaction. Because we are adding three carbons to our chain, the Grignard reagent we need must have three carbons on it. We can therefore rule out methyl grignard and ethyl grignard.
N-propyl is the straight-chained 3-carbon alkane, while isopropyl is branched. Looking at our final product, we can see the carbon chain we have added is straight-chained, and thus N-propyl Grignard is the best option. Because Grignard reagents are relatively basic, we must add an hydronium ion workup to protonate our alcohol.
This is an example of a Grignard reagent reaction. Because we are adding three carbons to our chain, the Grignard reagent we need must have three carbons on it. We can therefore rule out methyl grignard and ethyl grignard.
N-propyl is the straight-chained 3-carbon alkane, while isopropyl is branched. Looking at our final product, we can see the carbon chain we have added is straight-chained, and thus N-propyl Grignard is the best option. Because Grignard reagents are relatively basic, we must add an hydronium ion workup to protonate our alcohol.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The reaction of a Grignard reagent with ethylene oxide (oxirane) followed by work-up with dilute acid gives which of the following products?
The reaction of a Grignard reagent with ethylene oxide (oxirane) followed by work-up with dilute acid gives which of the following products?
The reaction of a Grignard reagent with oxirane (a type of epoxide) in addition to the work-up with dilute acid will yield a primary alcohol solely because there is a work-up with dilute acid. This shows that there is an excess of hydrogen, which will yield to a primary alcohol versus a secondary or tertiary alcohol.
The reaction of a Grignard reagent with oxirane (a type of epoxide) in addition to the work-up with dilute acid will yield a primary alcohol solely because there is a work-up with dilute acid. This shows that there is an excess of hydrogen, which will yield to a primary alcohol versus a secondary or tertiary alcohol.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

Predict the major product of the given Grignard reaction.

Predict the major product of the given Grignard reaction.
Grignard reagents (often formed in-situ due to their highly non-specific reactivity) act as reducing agents by forming carbanions, which are strong bases and nucleophiles. Nitriles may react with Grignard reagents to form imines. The reaction proceeds in an analogous fashion to a standard nucleophilic carbonyl addition, converting the triple bond to a double bond by forming an intermediate in which nitrogen carries a negative charge. A protic solvent, such as ethanol, is then added to neutralize the intermediate. Thus, the correct answer is the only compound in which an imine is formed, which is found in compound I.
Grignard reagents (often formed in-situ due to their highly non-specific reactivity) act as reducing agents by forming carbanions, which are strong bases and nucleophiles. Nitriles may react with Grignard reagents to form imines. The reaction proceeds in an analogous fashion to a standard nucleophilic carbonyl addition, converting the triple bond to a double bond by forming an intermediate in which nitrogen carries a negative charge. A protic solvent, such as ethanol, is then added to neutralize the intermediate. Thus, the correct answer is the only compound in which an imine is formed, which is found in compound I.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the product of the reaction shown?


What is the product of the reaction shown?


Step 1 converts the carboxylic acid into an ester.
Step 2 adds two equivalents of Grignard reagent: one to turn the molecule into acetone, and a second one to turn it into tert-butoxide. There is no way to stop the reaction after the first addition of Grignard reagent.
Step 3 will neutralize the base, leaving only t-butyl alcohol (I).
Step 1 converts the carboxylic acid into an ester.
Step 2 adds two equivalents of Grignard reagent: one to turn the molecule into acetone, and a second one to turn it into tert-butoxide. There is no way to stop the reaction after the first addition of Grignard reagent.
Step 3 will neutralize the base, leaving only t-butyl alcohol (I).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Acetaldehyde  undergoes a Wolf-Kishner reaction, which is the addition of hydrazine
undergoes a Wolf-Kishner reaction, which is the addition of hydrazine  with subsequent addition of a base and heat. In this reaction, the aldehyde is , resulting in a(n) product.
with subsequent addition of a base and heat. In this reaction, the aldehyde is , resulting in a(n) product.
Acetaldehyde 

The correct answer is that the aldehyde is reduced to an alkane. In viewing the final product, we see that acetaldehyde would be reduced to ethane. The reaction of any aldehyde or ketone with hydrazine and the subsequent addition of base and heat will result in that aldehyde or ketone being reduced to an alkane, and is referred to as the Wolf-Kishner reaction. The Wolf-Kishner reagent is a commonly tested reducing agent.
The correct answer is that the aldehyde is reduced to an alkane. In viewing the final product, we see that acetaldehyde would be reduced to ethane. The reaction of any aldehyde or ketone with hydrazine and the subsequent addition of base and heat will result in that aldehyde or ketone being reduced to an alkane, and is referred to as the Wolf-Kishner reaction. The Wolf-Kishner reagent is a commonly tested reducing agent.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

Determine the major product of the given intramolecular aldol reaction.


Determine the major product of the given intramolecular aldol reaction.

Keep in mind the following principles: Cyclization is favored when a five/six-member ring may be formed. Addition at an aldehyde is favored relative to the same reaction at a ketone.
As a result, abstraction of a hydrogen bound to carbon 6 (an alpha-carbon) is favored since the resulting carbanion may attack the aldehyde (carbon 1) to form a six-member ring, resulting in compound II. Compound I results from abstracting a hydrogen from carbon 2, generating a carbanion which may then attack the ketone. Based on the latter of the above principles, this is a minor product.
Keep in mind the following principles: Cyclization is favored when a five/six-member ring may be formed. Addition at an aldehyde is favored relative to the same reaction at a ketone.
As a result, abstraction of a hydrogen bound to carbon 6 (an alpha-carbon) is favored since the resulting carbanion may attack the aldehyde (carbon 1) to form a six-member ring, resulting in compound II. Compound I results from abstracting a hydrogen from carbon 2, generating a carbanion which may then attack the ketone. Based on the latter of the above principles, this is a minor product.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


What is the final organic product of the reaction shown?


First step: Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene
Second step: Formation of enolate
Third step: aldol addition (enolate attacks carbonyl carbon in benzaldehyde)
Fourth step: neutralization of anion and dehydration forming alkene
First step: Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene
Second step: Formation of enolate
Third step: aldol addition (enolate attacks carbonyl carbon in benzaldehyde)
Fourth step: neutralization of anion and dehydration forming alkene
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the product of the following reaction?

What is the product of the following reaction?
The reaction uses a Grignard reagent's nucleophilic carbon to attack the carbon in carbon dioxide. Following treatment with water the resulting molecule (a carboxylate anion, of the form  ) the carboxylate oxygen will be protonated, and the result is a carboxylic acid. Thus, the resulting molecule is a benzene ring with a carboxyl group attached (this is also known as benzoic acid).
) the carboxylate oxygen will be protonated, and the result is a carboxylic acid. Thus, the resulting molecule is a benzene ring with a carboxyl group attached (this is also known as benzoic acid).
The reaction uses a Grignard reagent's nucleophilic carbon to attack the carbon in carbon dioxide. Following treatment with water the resulting molecule (a carboxylate anion, of the form 
Compare your answer with the correct one above