Center, Shape, & Spread of Data - SAT Math
Card 0 of 47
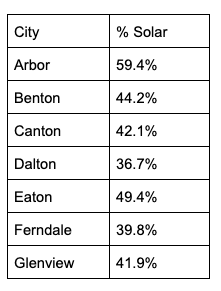
The table above displays, for seven cities in a certain state, the percentage of household electricity that comes from solar power. For the state as a whole, the median percentage is 44.9%. What is the difference between the statewide median percentage and the median percentage for these seven cities?

The table above displays, for seven cities in a certain state, the percentage of household electricity that comes from solar power. For the state as a whole, the median percentage is 44.9%. What is the difference between the statewide median percentage and the median percentage for these seven cities?
Tap to see back →
The median is the middle value in a set of data, so for this set of 7 cities you are looking for the 4th value once the values are arranged in order. The values in order are: 36.7, 39.8, 41.9, 42.1, 44.2, 49.4, 59.4. So the 4th/middle term is 42.1. Since the question asks for the difference between the median and 44.9, you subtract 44.9 - 42.1 to get the answer of 2.8.
The median is the middle value in a set of data, so for this set of 7 cities you are looking for the 4th value once the values are arranged in order. The values in order are: 36.7, 39.8, 41.9, 42.1, 44.2, 49.4, 59.4. So the 4th/middle term is 42.1. Since the question asks for the difference between the median and 44.9, you subtract 44.9 - 42.1 to get the answer of 2.8.
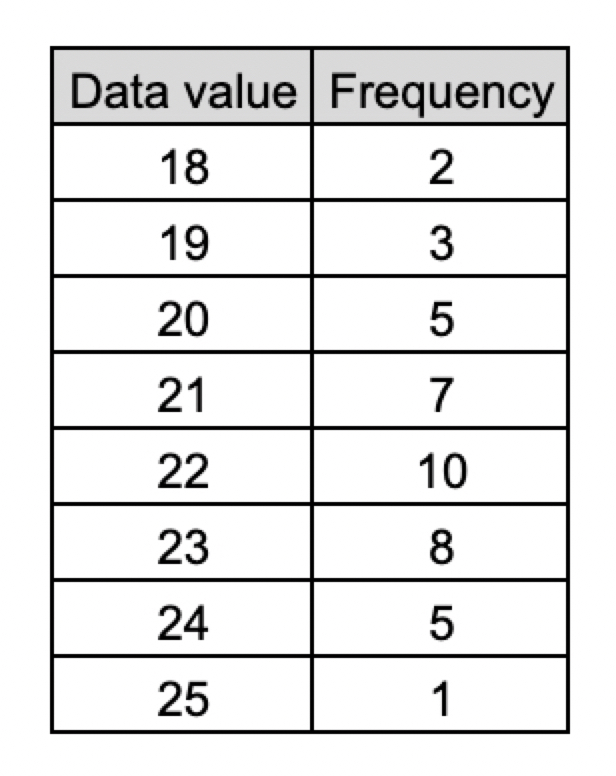
The frequency table summarizes the 41 data values in a data set. What is the maximum data value in the data set?

The frequency table summarizes the 41 data values in a data set. What is the maximum data value in the data set?
Tap to see back →
This question comes down to two key SAT concepts:
-
Understanding a frequency table. Frequency tables tell you how frequently each value occurs in a data table.
-
Read question stems carefully. Here they ask for the maximum data value, meaning you should only look at values in the "data value" column. And 25 - though it only occurs once - is the largest value in the data set and therefore the correct answer.
This question comes down to two key SAT concepts:
-
Understanding a frequency table. Frequency tables tell you how frequently each value occurs in a data table.
-
Read question stems carefully. Here they ask for the maximum data value, meaning you should only look at values in the "data value" column. And 25 - though it only occurs once - is the largest value in the data set and therefore the correct answer.
During a clearance sale, a retailer discounted the original price of its TVs by 25% for the first two weeks of the month, then for the remainder of the month further reduced the price by taking 20% off the sale price. For those who purchased TVs during the last week of the month, what percent of the original price did they have to pay?
During a clearance sale, a retailer discounted the original price of its TVs by 25% for the first two weeks of the month, then for the remainder of the month further reduced the price by taking 20% off the sale price. For those who purchased TVs during the last week of the month, what percent of the original price did they have to pay?
Tap to see back →
With percent problems, the key is often to make sure that you take the percent of the correct value. In this case, the initial 25% off means that customers will pay 75% of the original price. Then for the second discount, keep in mind that the discount is taken off of the sale price, not of the original price. So that's 20% off of the 75% that they did pay, which can be made easier by looking at what the customer does pay: 80% of the 75% sale price. Using fractions, that means they pay:  of the original price, which nets to
of the original price, which nets to  of the original price, or 60%.
of the original price, or 60%.
With percent problems, the key is often to make sure that you take the percent of the correct value. In this case, the initial 25% off means that customers will pay 75% of the original price. Then for the second discount, keep in mind that the discount is taken off of the sale price, not of the original price. So that's 20% off of the 75% that they did pay, which can be made easier by looking at what the customer does pay: 80% of the 75% sale price. Using fractions, that means they pay: 

Data: 2, 4, 8. Find median.
Data: 2, 4, 8. Find median.
Tap to see back →
4
4
Data: 3, 5, 7, 9. Find mean.
Data: 3, 5, 7, 9. Find mean.
Tap to see back →
$\frac{3+5+7+9}{4}=6$.
$\frac{3+5+7+9}{4}=6$.
General form of a linear model.
General form of a linear model.
Tap to see back →
$y = mx + b$.
$y = mx + b$.
How are outliers identified in a boxplot?
How are outliers identified in a boxplot?
Tap to see back →
Values more than 1.5 IQRs above $Q_3$ or below $Q_1$.
Values more than 1.5 IQRs above $Q_3$ or below $Q_1$.
How is IQR affected by outliers?
How is IQR affected by outliers?
Tap to see back →
Less affected than range or standard deviation.
Less affected than range or standard deviation.
If $r$ is near -1, what does that mean?
If $r$ is near -1, what does that mean?
Tap to see back →
Strong negative linear relationship.
Strong negative linear relationship.
If $r$ is near 0, what does that mean?
If $r$ is near 0, what does that mean?
Tap to see back →
Little or no linear relationship.
Little or no linear relationship.
If $r$ is near 1, what does that mean?
If $r$ is near 1, what does that mean?
Tap to see back →
Strong positive linear relationship.
Strong positive linear relationship.
If a phone plan costs $20$ per month plus a $30$ activation fee, write a linear cost model.
If a phone plan costs $20$ per month plus a $30$ activation fee, write a linear cost model.
Tap to see back →
$C = 20m + 30$.
$C = 20m + 30$.
If a population of 800 declines 3% per year, write the decay model.
If a population of 800 declines 3% per year, write the decay model.
Tap to see back →
$P = 800(0.97)^t$.
$P = 800(0.97)^t$.
If a substance halves every 10 years, write decay model.
If a substance halves every 10 years, write decay model.
Tap to see back →
$A = A_0(\tfrac{1}{2})^{t/10}$.
$A = A_0(\tfrac{1}{2})^{t/10}$.
If an investment of $1000$ grows by 5% per year, write the model for value after $t$ years.
If an investment of $1000$ grows by 5% per year, write the model for value after $t$ years.
Tap to see back →
$V = 1000(1.05)^t$.
$V = 1000(1.05)^t$.
If data are all identical, what is the standard deviation?
If data are all identical, what is the standard deviation?
Tap to see back →
0
0
If data are skewed left, which is larger: mean or median?
If data are skewed left, which is larger: mean or median?
Tap to see back →
The median is greater than the mean.
The median is greater than the mean.
If data are skewed right, which is larger: mean or median?
If data are skewed right, which is larger: mean or median?
Tap to see back →
The mean is greater than the median.
The mean is greater than the median.
If data are symmetric, how do mean and median compare?
If data are symmetric, how do mean and median compare?
Tap to see back →
They are approximately equal.
They are approximately equal.
If data have a large standard deviation, what does that indicate?
If data have a large standard deviation, what does that indicate?
Tap to see back →
The data are more spread out from the mean.
The data are more spread out from the mean.
If data have a small standard deviation, what does that indicate?
If data have a small standard deviation, what does that indicate?
Tap to see back →
The data are tightly clustered around the mean.
The data are tightly clustered around the mean.
If the population increases by 200 each year from 5,000, write the linear model.
If the population increases by 200 each year from 5,000, write the linear model.
Tap to see back →
$P = 5000 + 200t$.
$P = 5000 + 200t$.
If two data sets have same mean but different spreads, which has higher variability?
If two data sets have same mean but different spreads, which has higher variability?
Tap to see back →
The one with larger SD or IQR.
The one with larger SD or IQR.
If you add 5 to every value in a data set, how does the mean change?
If you add 5 to every value in a data set, how does the mean change?
Tap to see back →
Increases by 5.
Increases by 5.
If you add 5 to every value, how does standard deviation change?
If you add 5 to every value, how does standard deviation change?
Tap to see back →
It stays the same.
It stays the same.
If you multiply every value by 2, how does the mean change?
If you multiply every value by 2, how does the mean change?
Tap to see back →
It doubles.
It doubles.
If you multiply every value by 2, how does the standard deviation change?
If you multiply every value by 2, how does the standard deviation change?
Tap to see back →
It doubles.
It doubles.
What does $f(a) = b$ mean?
What does $f(a) = b$ mean?
Tap to see back →
When $x = a$, the function’s output is $b$.
When $x = a$, the function’s output is $b$.
What does it mean for a function to be one-to-one?
What does it mean for a function to be one-to-one?
Tap to see back →
Each output is produced by exactly one input (passes the horizontal line test).
Each output is produced by exactly one input (passes the horizontal line test).
What does standard deviation measure?
What does standard deviation measure?
Tap to see back →
The average distance of data points from the mean.
The average distance of data points from the mean.
What is interquartile range (IQR)?
What is interquartile range (IQR)?
Tap to see back →
$\text{IQR} = Q_3 - Q_1$.
$\text{IQR} = Q_3 - Q_1$.
What is the definition of standard deviation?
What is the definition of standard deviation?
Tap to see back →
Square root of variance; measures average distance from mean.
Square root of variance; measures average distance from mean.
What is the mean?
What is the mean?
Tap to see back →
The average: $\text{mean} = \frac{\text{sum of all values}}{\text{number of values}}$.
The average: $\text{mean} = \frac{\text{sum of all values}}{\text{number of values}}$.
What is the meaning of the symbol $\ge$?
What is the meaning of the symbol $\ge$?
Tap to see back →
Greater than or equal to.
Greater than or equal to.
What is the meaning of the symbol $\le$?
What is the meaning of the symbol $\le$?
Tap to see back →
Less than or equal to.
Less than or equal to.
What is the meaning of the symbol $<$?
What is the meaning of the symbol $<$?
Tap to see back →
Less than; the value on the left is smaller than the value on the right.
Less than; the value on the left is smaller than the value on the right.
What is the meaning of the symbol $>$?
What is the meaning of the symbol $>$?
Tap to see back →
Greater than; the value on the left is larger than the value on the right.
Greater than; the value on the left is larger than the value on the right.
What is the median?
What is the median?
Tap to see back →
The middle value when data are ordered.
The middle value when data are ordered.
What is the mode?
What is the mode?
Tap to see back →
The most frequently occurring value.
The most frequently occurring value.
What measure of spread is most resistant to outliers?
What measure of spread is most resistant to outliers?
Tap to see back →
Interquartile range (IQR).
Interquartile range (IQR).
What type of change occurs in a linear model?
What type of change occurs in a linear model?
Tap to see back →
Constant difference (additive) change.
Constant difference (additive) change.
A student claims, 'My school’s average SAT score is 1400, so every student scores around 1400.' What’s the flaw?
A student claims, 'My school’s average SAT score is 1400, so every student scores around 1400.' What’s the flaw?
Tap to see back →
Confuses mean with distribution; average doesn’t imply all are near that value.
Confuses mean with distribution; average doesn’t imply all are near that value.
Which measure of center is most affected by outliers?
Which measure of center is most affected by outliers?
Tap to see back →
The mean.
The mean.
Why might averages hide important details?
Why might averages hide important details?
Tap to see back →
They can mask variability or sub-group differences within the data.
They can mask variability or sub-group differences within the data.
When is a regression model appropriate?
When is a regression model appropriate?
Tap to see back →
When data show a roughly linear pattern and residuals are randomly scattered.
When data show a roughly linear pattern and residuals are randomly scattered.
Data: 1, 2, 2, 4. Find mode.
Data: 1, 2, 2, 4. Find mode.
Tap to see back →
2
2
Data: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9. Find mean and median.
Data: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9. Find mean and median.
Tap to see back →
Both are 5 (symmetric distribution).
Both are 5 (symmetric distribution).