Quartiles and Interquartile Range
Help Questions
SAT Math › Quartiles and Interquartile Range
Determine the interquartile range of the following numbers:
42, 51, 62, 47, 38, 50, 54, 43
None of these
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
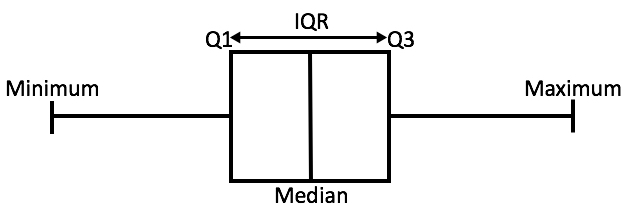
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.
Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
First reorder the numbers in ascending order:
38, 42, 43, 47, 50, 51, 54, 62
Then divide the numbers into 2 groups, each containing an equal number of values:
(38, 42, 43, 47)(50, 51, 54, 62)
Q1 is the median of the group on the left, and Q3 is the median of the group on the right. Because there is an even number in each group, we'll need to find the average of the 2 middle numbers:
The interquartile range is the difference between Q3 and Q1:
The interquartile range is the difference in value between the upper quartile and lower quartile.
Find the interquartile range of the following data set:
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
The first step (as with most data set problems) is to rearrange the data set from least to greatest value:

To find the lower quartile (

Thus, our lower quartile is at 
Since our 3rd number is 2, and our 4th number is 3, we need to find 1/4 of the way between 2 and 3. We will use the equation






Thus, our
We can repeat the process above to find the upper quartile (











So, our 
The last step is easy by comparison. Subtract 

Thus, our interquartile range is 
Find the interquartile range of the following set of numbers:
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
To find quartile range, you first need to isolate the numbers that are the book ends of your first and 3rd quartiles. To do this, find the middlenumber between the min and mean, and subtract this from the middle number between the mean and the max number. Thus,
Find the interquartile range of the data set above.
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
When asked to find the IQR of a set of data, we must first put the numbers in numerical order:

Now we need to divide the data set into the upper quartile and lower quartile, we do so by finding the mean which is the center value of the data set.
In this data set, our median is 
This means that our upper quartile consists of 
So our 

Our 

Thus, our IQR is 
Find the interquartile range of the following data set:
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
Find the median of the following data set:
Whenever we are working with a data set, it can be helpful to put the terms in order:
Now that our terms are in order, we can do all sorts of things with them.
In this case, we need the interquartile range. First let's find the median
In this case, we have an equal number of terms, so we need to find the average of the middle two.
So our median is 39
Next, we need to find the first and third quartiles. These are essentially the medians of each half of our data set.
First Quartile is easy. it is just 16 because our two middle values for the first half are 16:
Third Quartile
finally, our IQR is going to be the difference between our 1st and 3rd quartiles:
So our answer is 64





Using the data provided, find the Interquartile range, IQR.
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
The data set provided is called a five number summary.
These data values allow us to find the median, IQR, and range.
This question is asking for the IQR which is 

Using the data above, find the interquartile range.
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
The Interquartile range, or IQR, is defined as the 
The first step is the find the median of the data set, which in this case is 


For the upper quartile, if placed in numerical order
we see that there is an even number, thus we must take the center two numbers and find the average to find the true center of this data set, giving us


We do the same for the lower quartile, giving us a

When we subtract 


Using the data above, find the IQR. (interquartile range)
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
To find the IQR, we must first find the 

The 

thus the 


thus the 

So, 
Find the interquartile range given the data set above.
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
When asked to find the IQR of a set of data, we must first put the numbers in numerical order:

Now we need to divide the data set into the upper quartile and lower quartile, we do so by finding the median which is the center value of the data set.
In this data set, our median is 
This means that our upper quartile consists of 
So our 

Our 

Thus, our IQR is 
Using the data set above, find the interquartile range.
Explanation
How do you find the interquartile range?
We can find the interquartile range or IQR in four simple steps:
- Order the data from least to greatest
- Find the median
- Calculate the median of both the lower and upper half of the data
- The IQR is the difference between the upper and lower medians
Step 1: Order the data
In order to calculate the IQR, we need to begin by ordering the values of the data set from the least to the greatest. Likewise, in order to calculate the median, we need to arrange the numbers in ascending order (i.e. from the least to the greatest).
Let's sort an example data set with an odd number of values into ascending order.
Now, let's perform this task with another example data set that is comprised of an even number of values.
Rearrange into ascending order.
Step 2: Calculate the median
Next, we need to calculate the median. The median is the "center" of the data. If the data set has an odd number of data points, then the mean is the centermost number. On the other hand, if the data set has an even number of values, then we will need to take the arithmetic average of the two centermost values. We will calculate this average by adding the two numbers together and then dividing that number by two.
First, we will find the median of a set with an odd number of values. Cross out values until you find the centermost point
The median of the odd valued data set is four.
Now, let's find the mean of the data set with an even number of values. Cross out values until you find the two centermost points and then calculate the average the two values.
Find the average of the two centermost values.
The median of the even valued set is four.
Step 3: Upper and lower medians
Once we have found the median of the entire set, we can find the medians of the upper and lower portions of the data. If the data set has an odd number of values, we will omit the median or centermost value of the set. Afterwards, we will find the individual medians for the upper and lower portions of the data.
Omit the centermost value.
Find the median of the lower portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the lower portion is
Find the median of the upper portion.
Calculate the average of the two values.
The median of the upper potion is
If the data set has an even number of values, we will use the two values used to calculate the original median to divide the data set. These values are not omitted and become the largest value of the lower data set and the lowest values of the upper data set, respectively. Afterwards, we will calculate the medians of both the upper and lower portions.
Find the median of the lower portion.
The median of the lower portion is two.
Find the median of the upper portion.
The median of the upper portion is eight.
Step 4: Calculate the difference
Last, we need to calculate the difference of the upper and lower medians by subtracting the lower median from the upper median. This value equals the IQR.
Let's find the IQR of the odd data set.
Finally, we will find the IQR of the even data set.
In order to better illustrate these values, their positions in a box plot have been labeled in the provided image.

Now that we have solved a few examples, let's use this knowledge to solve the given problem.
Solution:
When asked to find the IQR of a set of data, we must first put the numbers in numerical order:

Now we need to divide the data set into the upper quartile and lower quartile, we do so by finding the median which is the center value of the data set.
In this data set, our median is 
This means that our upper quartile consists of 
So our 

Our 

Thus, our IQR is 































































































