All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Help With Sn2 Reactions
In reactions involving the alkylation of acetylide ions, it is preferred that the alkyl halide be primary. What is the reason for this?
The reaction involves a carbocation as intermediate
The mechanism for these reactions is SN2
The reactions generally occur in two steps
An answer cannot be determined without more information about the reaction conditions
The mechanism for these reactions is SN1
The mechanism for these reactions is SN2
The reason that the alkyl halide is preferred to be primary is because the mechanism for these reactions is SN2. SN2 indicates a substitution reaction that takes place in one step. A primary alcohol is preferred to prevent steric congestion caused by the simultaneous binding of the nucleophile and release of the leaving group. This reaction mechanism is faster because it omits the formation of a carbocation intermediate.
In contrast, SN1 reactions take place in two steps and involve the formation of a carbocation intermediate.
Example Question #1 : Elimination Reactions
Which of the following would be the best base to perform an E2 elimination?
Sodium butoxide
Sodium cyanide
Methanol
Potassium hydroxide
Ammonium
Sodium butoxide
The correct answer is sodium butoxide. Remember from your studies that for E2 reactions to be highly preferred they require a "big, bulky, base".
First eliminate ammonium 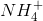
Now we can look at the real bases. Sodium cyanide will yield the cyanide ion, which is an extremely strong nucleophile. Remember that the E2 competes with the SN2. This means that the cyanide ion will prefer performing the SN2 not the E2, so we can cross this answer choice off.
Finally we are down to 2 answer choices, potassium hydroxide and sodium butoxide. Though potassium hydroxide is a strong base, it does not come close to the bulkiness of sodium butoxide. Thus, our best choice is sodium butoxide.
Example Question #52 : Reactions Types
For which of the following acid-base reactions will the equilibrium lie on the left side?

The pKa value indicates how strong an acid is, and acid strength increases as pKa decreases. The side of a reaction with a lower pKa is going to dissociate more, pushing the equilibrium over to the other side. The equilibrium will thus lie on the side with the HIGHER pKa.
Since the pKa of acetic acid (4.76) is higher than the pKa of trifluoroacetic acid (0), the reaction will shift to the left to reach equilibrium.
Example Question #1 : Oxidation Reduction Reaction
Which substance is used as a reducing agent?
A reducing agent is a substance that readily donates an electron to another substance. They consist primarily of elements with low electronegativities such as hydrogen. Therefore, the answer is 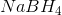
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources