All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Right Triangles
Solve for 
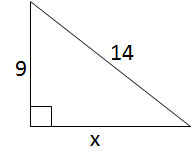
We will use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve for the missing side length.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
A square boxing ring has a perimeter of 






Since the perimeter of the ring is 

The distance between the two boxers in opposing corners is a straight line from any one corner to the other. That straight line forms the hypotenuse of a right triangle whose other two sides are each 
Solving for the length of the hypotenuse of this right triangle with the pythagorean theorem 
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
Given a right triangle with a leg length of 6 and a hypotenuse length of 10, find the length of the other leg, x.

4
64
8
16
8
Using Pythagorean Theorem, we can solve for the length of leg x:
x2 + 62 = 102
Now we solve for x:
x2 + 36 = 100
x2 = 100 – 36
x2 = 64
x = 8
Also note that this is proportionally a 3/4/5 right triangle, which is very common. Always look out for a side-to-hypoteneuse ratio of 3/5 or 4/5, or a side-to-side ratio of 3/4, in any right triangle, so that you may solve such triangles rapidly.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
In a right triangle a hypotenuse has a length of 8 and leg has a length of 7. What is the length of the third side to the nearest tenth?
Using the pythagorean theorem, 82=72+x2. Solving for x yields the square root of 15, which is 3.9
Example Question #141 : Geometry
Given a right triangle with a leg length of 2 and a hypotenuse length of √8, find the length of the other leg, x.

10
6
2
√8
4
2
Using Pythagorean Theorem, we can solve for the length of leg x:
x2 + 22 = (√8)2 = 8
Now we solve for x:
x2 + 4 = 8
x2 = 8 – 4
x2 = 4
x = 2
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
The legs of a right triangle are 

Use the Pythagorean Theorem. The sum of both legs squared equals the hypotenuse squared.
Example Question #1 : Right Triangles
Use the Pythagorean theorem: 
We know the length of one side and the hypotenuse.
Now we can solve for the missing side.
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
A right triangle has one side equal to 5 and its hypotenuse equal to 14. Its third side is equal to:
13.07
9
14.87
171
12
13.07
The Pythagorean Theorem gives us a2 + b2 = c2 for a right triangle, where c is the hypotenuse and a and b are the smaller sides. Here a is equal to 5 and c is equal to 14, so b2 = 142 – 52 = 171. Therefore b is equal to the square root of 171 or approximately 13.07.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
Which of the following could NOT be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle?
5, 12, 13
14, 48, 50
12, 16, 20
5, 7, 10
8, 15, 17
5, 7, 10
We use the Pythagorean Theorem and we calculate that 25 + 49 is not equal to 100.
All of the other answer choices observe the theorem a2 + b2 = c2
Example Question #101 : Triangles
Which set of sides could make a right triangle?
10, 12, 16
9, 12, 15
6, 7, 8
4, 6, 9
9, 12, 15
By virtue of the Pythagorean Theorem, in a right triangle the sum of the squares of the smaller two sides equals the square of the largest side. Only 9, 12, and 15 fit this rule.
Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources




















 .
.











