All Common Core: 8th Grade Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #323 : Intermediate Single Variable Algebra
Solve the equation:
To solve the quadratic equation, 





Example Question #1 : Understand Functions: Ccss.Math.Content.8.F.A.1
Solve for 
The solution is undefined.
To factor this equation, first find two numbers that multiply to 35 and sum to 12. These numbers are 5 and 7. Split up 12x using these two coefficients:
Example Question #1 : Functions
Solve for 
To find 
Example Question #2 : Functions
Solve for 
To find 
Example Question #3 : Functions
Which of the following equations represents a one-to-one function:
Only equation B maps each value of 



Example Question #4 : Functions
Find 
Undefined
This question demonstrates that complicated functions are not complicated at every point.
To solve the function at x=1, all that is necessary is familiarity with the operations used.
Example Question #5 : Functions
Define 
Evaluate 
To evaluate 
Example Question #6 : Functions
Define
Which of the following is equivalent to 
To solve this problem replace every x in 

Therefore,
Example Question #1 : Functions
Select the table that properly represents a function.





Each of the tables provided contains sets of ordered pairs. The input column represents the x-variables, and the output column represents the y-variables. We can tell if a set of ordered pairs represents a function when we match x-values to y-values.
In order for a table to represents a function, there must be one and only one input for every output. This means that our correct answer will have all unique input values:

Functions cannot have more than one input value that is the same; thus, the following tables do not represent a function:



Example Question #1 : Functions
Select the table that properly represents a function.





Each of the tables provided contains sets of ordered pairs. The input column represents the x-variables, and the output column represents the y-variables. We can tell if a set of ordered pairs represents a function when we match x-values to y-values.
In order for a table to represents a function, there must be one and only one input for every output. This means that our correct answer will have all unique input values:

Functions cannot have more than one input value that is the same; thus, the following tables do not represent a function:



All Common Core: 8th Grade Math Resources













































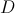


![f(x) = \frac{x^{4}-x+\sqrt[3]{x}}{x^{x}+3x}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/434992/gif.latex)




![f(1) = \frac{1^{4}-1+\sqrt[3]{1}}{1^{1}+3(1)}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/434994/gif.latex)























