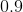All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Square A Decimal
Which quantity is greater? When
Quantity A

Quantity B
1
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Quantity A is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
X must equal a number between 0 and 1.
If you square any decimal number in this range you will get an answer less than 1. Try 
Therefore Quantity B is always larger.
Example Question #2 : How To Square A Decimal
Which is greater, when
Quantity A
Quantity B
The two quantities are equal
Quantity A is greater
Quantity B is greater
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
When 



When
But when
Therefore we cannot tell which is greater based on the information given.
Example Question #963 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
Which is greater, when
Quantity A
Quantity B
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
Quantity A is greater
The two quantities are equal
Quantity B is greater
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
When 



When
But when
Therefore we cannot tell which is greater based on the information given.
Example Question #2 : How To Square A Decimal
Which is greater, when
Quantity A
Quantity B
Quantity B is greater
The two quantities are equal
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
Quantity A is greater
Quantity A is greater
When 










Quantity A is greater.
Example Question #3 : How To Square A Decimal
Which is greater, when
Quantity A
Quantity B
Quantity B is greater
Quantity A is greater
The two quantities are equal
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given
Quantity B is greater
When 




Quantity B is greater.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Square Root Of A Decimal
Find the square root of the following decimal:
The easiest way to find the square root of a fraction is to convert it into scientific notation.
The key is that the exponent in scientific notation has to be even for a square root because the square root of an exponent is diving it by two. The square root of 9 is 3, so the square root of 8.1 is a little bit less than 3, around 2.8
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Square Root Of A Decimal
Find the square root of the following decimal:
To find the square root of this decimal we convert it into scientific notation.
Because 
Example Question #4 : Basic Squaring / Square Roots
Find the square root of the following decimal:
This problem can be solve more easily by rewriting the decimal into scientific notation.
Because 
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Square Root Of A Decimal
Find the square root of the following decimal:
This problem becomes much simpler if we rewrite the decimal in scientific notation
Because 
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Square Root Of A Decimal
Find the square root of the following decimal:
To find the square root of this decimal we convert it into scientific notation.
Because 
All GRE Math Resources