All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #31 : Reactions By Reactant
What is the product of the reaction between 2-butanone and lithium aluminum hydride?
None of these
3-butanol
3-butanone
2-butanol
Butane
2-butanol
Lithium aluminum hydride is a reducing agent. It reduces ketones and carboxylic acids to alcohols. 2-butanone is a 4-carbon chain with a double bond between an oxygen and carbon 2. The reduction turns the double bond with oxygen into a single bond to a hydroxy group. This makes the product 2-butanol.
Example Question #1 : Carbonyl Reactants

Choose the appropriate starting compound based on the reaction conditions and major product shown in the figure.

Either I or II
I only
III only
II only
IV only
IV only
In the presence of a strong base and benzene, ethylene glycol will convert ketones to acetals as seen in the product shown above. The given reagents will not react with esters or alcohols. The only given compound containing a ketone is molecule IV, the correct answer. This type of reaction is useful in organic synthesis when reaction at an ester is desired, but a ketone must be protected from reacting simultaneously. The acetal formed is often called a protecting group and may be reversed by addition of acid.
Example Question #2 : Carbonyl Reactants

Which of the labeled hydrogens in the given molecule is the most acidic?
C
A
D
B
C
This question is asking what the most acidic hydrogen is in an aldehyde. To identify the most acidic hydrogen, we'll need to consider which conjugate base will be the most stable after the loss of hydrogen. When the alpha-hydrogen is lost, the resulting carbanion will be the most stabilized due to resonance with the adjacent carbonyl group. This resonance helps to distribute the negative charge on the carbanion over a greater area, which contributes to the greater stability of this conjugate base. Abstraction of a hydrogen from any of the other position would result in a carbanion that could not participate in resonance and thus would not be as stable.
Example Question #41 : Reactions By Reactant

What is the product of the given reaction?


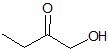

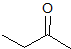

This is a Grignard reagent carbon-carbon bond forming reaction. This reaction is being used with an ester which goes through a ketone intermediate with requires a second attack form the organolithium to reduce to an alcohol. Esters and acyl chlorides go to an alcohol with two of the same R groups from the organolithium in a Grignard reaction. This structure fits the bill:
Example Question #5 : Carbonyl Reactants

If the given compound is reacted with 






LiAlH4 is a very strong reducing agent and it is a reactant that can reduce acyl chlorides into alcohols. There are 2 alcohols to choose from and now it needs to be known that LiAlH4 doesn't add anything but hydrogens to its substrate. (Note that in the correct answer, there is another H that is not drawn on the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group).
Example Question #1 : Carbonyl Reactants

What is the product of the reaction given?





Below is the mechanism for the reaction given which is called the McMurry Reaction. It is a titanium (Ti) prompted pinacol coupling followed by deoxygenation.

Example Question #7 : Carbonyl Reactants

In an aprotic solvent, what would be the product of the reaction given?





This reaction involves the generation of a radical by single electron transfer that couple through carbon-carbon bond formation to form the product pinacol. This reaction as shown below occurs in an aprotic solvlent:

Example Question #1 : Help With Aldehyde And Ketone Reactions

What is the product of the reaction given?





Below is the mechanism for the reaction given which is called the McMurry Reaction. It is a titanium (Ti) prompted pinacol coupling followed by deoxygenation.

Example Question #1 : Help With Ether And Ester Reactions

Predict the major product of the following reaction (the reaction is allowed to run to completion and the final step is an acid workup).
IV
I
III
II
None of these
III
Alkyl lithium (organolithium) reagents are powerful reducing agents and react much in the same manner as Grignard reagents through the formation of a carbanion. In the first step of the reaction, the carbanion attacks at the carbonyl, creating a charged intermediate, which is neutralized by reformation of the carbonyl and the release of ethoxide (the ester chain is the leaving group). However, the alkyl lithium reagent continues the reaction by attacking at the carbonyl once again. This time, there is no suitable leaving group (every group bound is a carbon chain) and the intermediate remains until a proton transfer is facilitated to neutralize the oxygen's charge.
Example Question #1 : Help With Ether And Ester Reactions
When butanol is reacted with pentanoic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst, what would be the expected major product?
Butyl pentanoate
Butanoic acid
Pentene
Butene
Butyl pentanoate
To answer this question, it's important to consider what types of molecules are reacting. The pentanoic acid is a carboxylic acid, and the butanol is an alcohol. When carboxylic acids are reacted with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst, the result is an ester.
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources




