All AP Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Enthalpy
Which of the following statements is true concerning a chemical reaction?
Endothermic reactions have lower activation energies than exothermic reactions
The 

A catalyst reduces the enthalpy change for the reaction
Exothermic reactions are always spontaneous
The 

When a chemical reaction is represented graphically, we see that the enthalpy change is reversed between the forward and reverse reactions. If a reaction produces energy in a forward process, it will require an input of energy in the reverse process, and vice versa.
A catalyst only affects the rate of a chemical reaction; it does not affect the equilibrium. Finally, exothermic reactions are not always spontaneous, but will have lower activation of energies compared to endothermic reactions.
Example Question #1 : Enthalpy
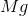

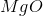
What is the change in enthalpy for the following reaction?
The change in enthalpy is calculated by:
When 
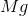

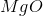
It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in enthalpy of a reaction.
Example Question #21 : Thermodynamics
The formation of nitrogen dioxide is a two step process.


The net reaction is 
What is the change in enthalpy when creating four moles of nitrogen dioxide?
Hess's law states that the change in enthalpy for a total reaction can be considered equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for every step involved in the reaction. In other words, we can determine the enthalpy change for nitrogen dioxide by adding the enthalpy changes for both steps involved in its formation.
This gives us the total change in enthalpy for the listed reaction, 
Example Question #1 : Enthalpy
Calculate ΔH for the following reaction:
CH4 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
Compound ΔH
CH4 (g) -74.8 kJ/mol
H2O (l) -285.8 kJ/mol
CO2 (g) -393.5 kJ/mol
not enough information
-890.3 kJ/mol
604.5 kJ/mol
-604.5 kJ/mol
889.7 kJ/mol
-890.3 kJ/mol
ΔH = Σ ΔHf products - Σ ΔHf reactants
ΔHf O2 or any element is 0
First step is to balance the equation:
CH4 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
ΔH = Σ ΔHf products - Σ ΔHf reactants
= [-393.5 kJ/mol + 2(-285.8) kJ/mol] - (-74.8 kJ/mol)
= -890.3 kJ/mol
Example Question #2 : Enthalpy



What is the change in enthalpy for the given reaction?
The change in enthalpy is calculated by:
When 



Since the reactions are in the correct order, adding all the 

Example Question #4 : Enthalpy



What is the change in enthalpy for the following reaction?
The change in enthalpy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in enthalpy of a reaction.
Example Question #2 : Enthalpy



What is the enthalpy of the following reaction?
The change in enthalpy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in enthalpy of a reaction. For this particular reaction, since there are two moles of product, the enthalpy of formation for 
Example Question #62 : Thermochemistry And Kinetics



What is the change in enthalpy for the following reaction?
The change in enthalpy is calculated by:
When 



It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in enthalpy of a reaction.
Example Question #1 : Enthalpy




What is the change in enthalpy for the following reaction?
The change in enthalpy is calculated by:
When 




It is important to first balance the reaction before performing calculations. The coefficients are important in determining the change in enthalpy of a reaction.
Example Question #1 : Enthalpy
Consider the following combustion reaction:
The following list is the enthalpies of formation for the compounds:
If one mole of propane is burned, what is the enthalpy of the reaction?
Since we have the enthalpies of formation, we can find the enthalpy of the reaction using the following equation:
We will need to use the coefficients from the balanced equation to calculate the enthalpy.
Since oxygen gas is elemental, it does not have an enthalpy of formation, and is omitted from the equation.
Certified Tutor
All AP Chemistry Resources










































































































