All AP Human Geography Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Models Of City Structure & Urban Development
Which of the following occupies the shaded area on the Concentric Zone Model shown here?

Working-Class Residential Zone
Transition Zone
Central Business District
Commuter Zone
Zone of Better Residences
Transition Zone
The Transition Zone is characterized as industrial and typically dominated by manufacturing facilities. It surrounds the mainly commercial city center and is surrounded by working-class residential housing, maximizing access to markets to sell manufactured goods and housing for factory workers.
Example Question #681 : Ap Human Geography
Which of the following is the name of the zone shaded in the provided Concentric Zone Model?

Central Business District Zone
Working Class Residential Zone
Middle-Income Residential Zone
Commuter Zone
Transition Zone
Commuter Zone
The outermost ring of the Concentric Zone Model is commuter-residential and consists mainly of low-density, estate-style housing, usually comprised of high-income professionals. Urban overcrowding is typically unappealing to people, so property values for low-density and spacious estates will be at a higher premium than higher-density urban properties.
Example Question #2 : Models Of City Structure & Urban Development
According to the Burgess Concentric Zone model, which zone are low-income residents most likely to inhabit and why?
The Working-Class Residential Zone, because conditions of on-site factory housing tend to be dreadful and violate OHSA safety standards
The Transition Zone, because marketplaces and businesses tend to develop near low-income residential areas to make profit on consumer goods and services
The Transition Zone, because of its close proximity to industrial and manufacturing jobs in the Central Business District
The Commuter Zone, because demand for housing close to jobs in the Central Business District has inflated urban housing prices
The Working-Class Residential Zone, because most cities have strict urban zoning laws that prohibit people from inhabiting areas that are zoned as light-industrial or commercial
The Transition Zone, because of its close proximity to industrial and manufacturing jobs in the Central Business District
The Transition Zone consists largely of low-quality housing that is close in proximity to industrial and manufacturing jobs in the Commercial Business District (CBD). Since the housing in this zone tends to be unpleasant, its cost is low and the proximity to entry-level jobs attracts low-income families. The Working-Class and Commuter Zones often consist of higher-quality housing, but the cost of living is often inflated and getting to the jobs often requires an automobile, which many low-income families cannot afford.
Example Question #681 : Ap Human Geography
Which of the following real-world examples is the most accurate example of people living in a Transition Zone?
The first concept of an American suburb involved estate-like villas located on the outskirts of big cities and occupied by wealthy business owners who could afford large parcels of land.
In most American cities, affordable apartments and living spaces are often in close proximity to light-commercial areas and office buildings that employ most people.
One of the benefits for faculty at many universities is on-campus housing near work at rates either subsidized or well below market value.
During the 1990s, China experienced an influx of rural residents migrating to industrial centers of big cities to work at manufacturing facilities, often living in slums or company housing.
Due to the frustration of overcrowding and traffic congestion, many people who work in San Francisco in fact take the train or metro rail from surrounding bedroom communities.
During the 1990s, China experienced an influx of rural residents migrating to industrial centers of big cities to work at manufacturing facilities, often living in slums or company housing.
The Transition Zone is composed of poor-quality housing for low-income residents in close proximity to commercial and industrial areas. Rural migrants to China's big industrial cities are typically living in poor-quality, low-cost housing very close to the factories at which they work, which best represents the Transition Zone of the Burgess Model.
Example Question #682 : Ap Human Geography
Which of the following models does the Burgess Concentric Zone Model most clearly resemble?
The Von Thunen Land Use Model
The Hoyt Sector Model
The Multiple Nuclei Model
The Demographic Transition Model
The Human Population Pyramid of a developing country
The Von Thunen Land Use Model
Both the Von Thunen and Burgess models consist of a circular pattern of ring-shaped zones that are designated based upon their value, significance, and accessibility to the central business/market areas of a settlement. The Von Thunen model prioritizes perishability of goods and accessible fuel sources (lumber) to the central populated area, while the Burgess model prioritizes accessibility of labor to industrial/commercial areas. Both result in a circular, layered model.
Example Question #11 : Cities & Urban Land Use
A city that has varying levels of development emanating in rings from a central business district is called a __________ city.
Multiple-Nuclei Model
Concentric Zone Model
Postmodernist
Sector Model
Beaux arts
Concentric Zone Model
A city that is described as a Concentric Zone Model city will have a central business district which is surrounded by a series of rings with varying levels of development. Generally the closest ring will be for low quality housing and the furthest ring will be for suburban housing.
Example Question #691 : Ap Human Geography
Which of these is not a characteristic of a central business district?
high property costs
high density of people during working hours
large number of residences
the first zone of the concentric zone model
large concentration of nonresidential activities
large number of residences
The central business district (CBD) is where a large amount of businesses are located. In the concentric zone model, it is located in the center of the city. Houses and apartments are less common in the CBD and tend to be more prevalent outside of it.
Example Question #1 : Burgess Concentric Zone Model
In the concentric zone model, what is the outermost zone?
working class zone
commuter zone
transitional zone
central business district
residential zone
commuter zone
The outermost zone of the concentric zone model is the commuter zone, which includes the suburbs. These are the people who live furthest away from the central business district and therefore have to commute the greatest distance to work.
Example Question #1 : Models Of City Structure & Urban Development
In Hoyt's Sector Model, where is the factory/industry zone located?
between the low class residential zone and the middle class residential zone
surrounded by the low class residential zone, and touching the central business district
right outside of the transitional zone
between the central business district and the high class residential zone
completely surrounding the central business district
surrounded by the low class residential zone, and touching the central business district
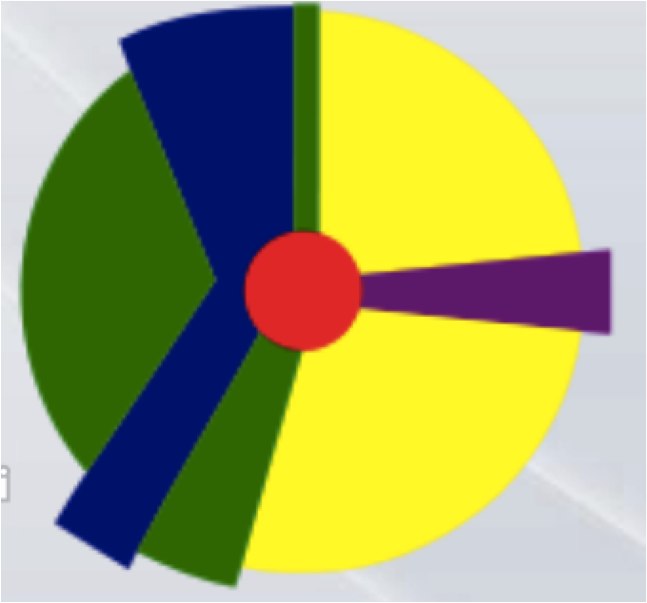
The factory/industry zone is the blue on the left, and it is located surrounded by the low class residential zone (green) and touching the central business district (red).
Example Question #1 : Harris & Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
A city that is divided up into several distinct neighborhoods and that lacks a centralized downtown area is best described as a __________ city.
Modernist
Sector Model
Concentric Zone Model
Postmodernist
Multiple-Nuclei Model
Multiple-Nuclei Model
A city that lacks a centralized business district or downtown area and that has several distinct neighborhoods that all act as regional centers within one larger city is best captured using the “Multiple-Nuclei Model.”
All AP Human Geography Resources




