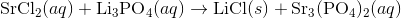All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Liquids And Solutions
Write an equation for the precipitation reaction that occurs (if it occurs) when a solution of strontium chloride is mixed with a solution of lithium phosphate.
Start by writing out the the chemical formulas for the reactants:
In order to figure out the possible products, combine the cation of one molecule with the anion of the other molecule.
For this reaction, the possible products are 

Next, use solubility rules to figure out if any precipitate is formed. Since compounds with 




Thus, we can write the final chemical equation:
Example Question #3 : Liquids And Solutions
Which of the following is insoluble in water?
Recall the solubility rules:


Example Question #4 : Liquids And Solutions
Which of the following substances is insoluble in aqueous solution?
Solubility rules can help us find the answer to this question.
First, solubility rules state that all compounds of Group 1A elements on the periodic table are soluble in aqueous solution. This means that all of the alkali metals, including potassium, form compounds which are soluble in aqueous solution; thus, 
Solubility rules also tell us that all ammonium salts (salts of 

Next, solubility rules tell us that all bromide salts are soluble, except for those of 




Example Question #5 : Liquids And Solutions
Which of the following is not readily soluble in water?
Remember the solubility rules for ionic solids in water:
1) Salts of group 1 (with few exceptions) and NH4+ are soluble
2) Nitrates, acetates, and perchlorates are soluble
3) Salts of silver, lead, and mercury (I) are insoluble
4) Chlorides, iodides, and bromides are soluble
5) Carbonates, phosphates, sulfides, oxides, and hydroxides are insoluble. Exceptions: sulfides of group 2 cations and hydroxides of calcium, strontium, and barium are slightly soluble
6) Sulfates are soluble except for those of calcium, strontium, and barium
Following these rules, we see that MgOH is insoluble in water
All College Chemistry Resources