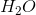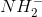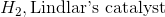All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Organic Chemistry
What is the best reagent for abstracting a hydrogen from ethyne?
None of these
The triple bond in ethyne makes the hydrogens slightly more acidic than those found in ethane. A very strong base, such as the conjugate base of ammonia, would be able to abstract that hydrogen. The abstraction turns the base into ammonia. It also creates a carbanion that can be used for chain extension and alkyne synthesis.
Example Question #171 : Gre Subject Test: Chemistry

What is the product of the compound when it reacts with two equivalents of base?
2-pentene
2-pentyne
None of these
1-pentene
1-pentyne
2-pentyne
For each equivalent of base, a pi bond is formed between the carbons initially bound to the bromine atoms. For each bond formed, a bromine leaving group leaves the hydrocarbon. One equivalent of base abstracts a hydrogen. The electrons from the bond to the hydrogen create a pi bond. This occurs twice, and a triple bond is formed. The result is a 5-carbon chain with a triple bond between the second and third carbons. This molecule is 2-pentyne.
Example Question #11 : Functional Group Reactions
Starting with an alkyne, synthesis of a cis alkene is driven upon addition of which of the following reagents?
Reduction of an alkyne with hydrogen and Lindlar's catalyst will result in a cis alkene. While 
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources