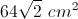All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Squares
ABCD and EFGH are squares such that the perimeter of ABCD is 3 times that of EFGH. If the area of EFGH is 25, what is the area of ABCD?
225
75
15
25
5
225
Assign variables such that
One side of ABCD = a
and One side of EFGH = e
Note that all sides are the same in a square. Since the perimeter is the sum of all sides, according to the question:
4a = 3 x 4e = 12e or a = 3e
From that area of EFGH is 25,
e x e = 25 so e = 5
Substitute a = 3e so a = 15
We aren’t done. Since we were asked for the area of ABCD, this is a x a = 225.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Square
A square has an area of 36. If all sides are doubled in value, what is the new area?
72
108
132
144
48
144
Let S be the original side length. S*S would represent the original area. Doubling the side length would give you 2S*2S, simplifying to 4*(S*S), giving a new area of 4x the original, or 144.
Example Question #231 : Plane Geometry
If the perimeter of a square is equal to twice its area, what is the length of one of its sides?
Area of a square in terms of each of its sides:
Area = S x S
Perimeter of a square:
Perimeter = 4S
So if 'the perimeter of a square is equal to twice its area':
2 x Area = Perimeter
2 x [S x S] = [4S]; divide by 2:
S x S = 2S; divide by S:
S = 2
Example Question #2 : Squares
Freddie is building a square pen for his pig. He plans to buy x feet of fencing to build the pen. This will result in a pen with an area of p square feet. Unfortunately, he only has enough money to buy one third of the planned amount of fencing. Which expression represents the area of the pen he can build with this limited amount of fencing?
9p
p/3
3p
p/9
p/6
p/9
If Freddie uses x feet of fencing makes a square, each side must be x/4 feet long. The area of this square is (x/4)2 = x2/16 = p square feet.
If Freddie uses one third of x feet of fencing makes a square, each side must be x/12 feet long. The area of this square is (x/12)2 = x2/144 = 1/9(x2/16) = 1/9(p) = p/9 square feet.
Alternate method:
The scale factor between the small perimeter and the larger perimeter = 1 : 3. Since we're comparing area, a two-dimensional measurement, we can square the scale factor and see that the ratio of the areas is 12 : 32 = 1 : 9.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Square
If the diagonal of a square measures 
This is an isosceles right triangle, so the diagonal must equal 

Example Question #274 : New Sat
A square 





The area of 





Example Question #2 : How To Find The Area Of A Square
The perimeter of a square is 
The perimeter of a square is given by 


So the area of the new square is given by 
Example Question #381 : Plane Geometry
How much more area does a square with a side of 2r have than a circle with a radius r? Approximate π by using 22/7.
4/7 square units
1/7 square units
12/14 square units
6/7 square units
6/7 square units
The area of a circle is given by A = πr2 or 22/7r2
The area of a square is given by A = s2 or (2r)2 = 4r2
Then subtract the area of the circle from the area of the square and get 6/7 square units.
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Area Of A Square
If the perimeter of a square is 44 centimeters, what is the area of the square in square centimeters?
Since the square's perimeter is 44, then each side is 
Then in order to find the area, use the definition that the
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Square

Given square 
Assume that the length of each midpoint is 1. This means that the length of each side of the large square is 2, so the area of the larger square is 4 square units.
To find the area of the smaller square, first find the length of each side. Because the length of each midpoint is 1, each side of the smaller square is 

The area then of the smaller square is 2 square units.
Comparing the area of the two squares, the larger square is 2 times larger than the smaller square.
Certified Tutor
All High School Math Resources