All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Help With Carboxylic Acid Synthesis
Which of the following reactions would NOT produce a carboxylic acid?
PCC is considered a weak oxidizing agent. The reaction of a primary alcohol with PCC would only yield an aldehyde, while reaction with a secondary alcohol will yield a ketone. PCC will not be used to generate carboxylic acids.
A stronger oxidation, like 

Example Question #2 : Help With Carboxylic Acid Synthesis
Which one of the following compounds can produce a carboxylic acid only when reacted with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid?
1-pentanol
2-pentanone
2-pentanol
2-methylpentan-2-ol
Pentanal
1-pentanol
After recognizing the reagents given, we know we need to begin with an alcohol. The alcohol choices differ only by how substituted they are.
For a carboxylic acid to form from a reaction with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid, a primary alcohol needs to be available. Therefore, 1-pentanol is the correct answer.
Example Question #1 : Carbonyls
When 3-chloroheptane undergoes malonic ester synthesis, the final product is __________.
nonanoic acid
malonic ester
a ten-carbon ketone
None of the other answers
3-ethylheptanoic acid
3-ethylheptanoic acid
The malonic ester is deprotonated at the most acidic hydrogen, the one on the carbon between the two oxygens. The electrons from that bond to the hydrogen form a carbon-carbon double bond while electrons from the oxygen-carbon double bond go to the oxygen atom. This is the enolate form. The chlorine leaves the 3-chloroheptane and the electrons from the carbon-carbon double bond bond to the carbon that the chlorine left. At the same time, the carbonyl is reformed. After deesterfication, 3-ethylheptanoic acid is formed.
Example Question #11 : Carbonyl Products
Which of the following is not a derivative of a carboxylic acid?
Aldehyde
All of these are carboxylic acid derivatives
Ester
Amide
Aldehyde
Aldehyde is not a derivative of carboxylic acid. Esters can be derived from carboxylic acids by reacting them with 



Example Question #12 : Carbonyl Products
Which of the following reagents is needed to convert an amide into a carboxylic acid?
All of these
As a general rule, any carboxylic acid derivative can be converted into al carboxylic acid when reacting with
Example Question #13 : Carbonyl Products

What is the product of the given reaction?
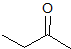





The hydrolyzation of a nitrile with hydronium leads to a carboxylic acid. Only one choice is a carboxylic acid.
Example Question #14 : Carbonyl Products
Please choose the best answer for the following question.
Which of the following reagents is best for converting a primary alcohol to a carboxylic acid?

PCC


Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources
















