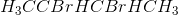All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #511 : Organic Chemistry
2-butene reacts with 
No reaction
Here we have a classic electrophilic addition reaction.
We must remember that a double bond is an area in a molecule that has a high electron density. As a result, double bonds can act as nucleophiles and react with good electrophiles.
In this problem, the alkene attacks the dibromide to form a bromonium ion, which is rather unstable. The bromonium ion pulls carbon's electrons toward itself, causing the carbons in the bromonium complex to have a slightly negative charge. As a result, the negatively charged bromine can attack either of the carbon atoms and, thus, we have added two bromines to our carbon chain.
Example Question #1 : Other Reaction Mechanisms
How many stable resonance structures are there for the following molecule (include the given structure in your total count)?

6
5
4
1
3
5
The five resonance structures of the given molecule are shown below:

Example Question #2 : Other Reaction Mechanisms
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution.

IV, V, I, III, II
V, II, I, III, IV
V, I, III, IV, II
II, IV, III, I, V
II, I, III, IV, V
V, I, III, IV, II
The nitro substituent is strongly deactivating, ketones are moderately deactivating substituent, halides are weakly deactivating, alkyl groups are weakly activating, and amine groups are strongly activating.
Example Question #1 : Identifying Reaction Mechanisms
Which of these would react fastest with methanol via an SN1 mechanism?
All of these will react with similar rates when undergoing an SN1 reaction with methanol
An SN1 mechanism involves the leaving of the bromine in the first step and the formation of a carbocation on that carbon. The molecule with the most stable carbocation will react most quickly.
The carbocation is most stable on the most highly substituted carbon. All the of the answer options form primary or secondary cations except for one. The correct answer has a carbocation on a carbon bonded to two methyl groups and one ethyl group. The correct answer is 
Example Question #3 : Other Reaction Mechanisms

What is the major product of the reaction shown above?





Grignard reagents attack ketones at the site of the ketone's carbon to produce tertiary alcohols.
Example Question #2 : Identifying Reaction Mechanisms
Under which of the following sets of conditions is an SN2 reaction most favored?
Ether solvent, primary electrophile, strong nucleophile
Methanol solvent, tertiary electrophile, weak nucleophile
Acetone solvent, tertiary electrophile, strong nucleophile
DMSO solvent, primary electrophile, weak nucleophile
Ethanol solvent, primary electrophile, strong nucleophile
Ether solvent, primary electrophile, strong nucleophile
SN2 reactions require a strong nucleophile. If the the nucleophile is weak, SN1 is favored over SN2.
For SN2 reactions less substitution in the electrophile is favored (methyl > primary > secondary).
For SN2 reactions polar aprotic solvents are preferred (DMSO, acetone, DMF and ethers are common polar aprotic solvents). Polar protic solvents (ethanol, methanol) favor SN1 reactions.
Example Question #7 : Other Reaction Mechanisms
Consider the generic reaction shown below.
What type of reaction is occurring here?
Elimination
Substitution
Rearrangement
Addition
Substitution
In this question, we're presented with a hypothetical reaction, and we're asked to identify which type of reaction is occurring. Let's go through each of the answer choices to see which one fits.
Addition reactions are ones in which two atoms or molecules come together. It takes the form of 
Elimination reactions are essentially the opposite of addition reactions. In this case, a molecule splits into two, taking the form of 
Rearrangement reactions are ones in which the reactant is manipulated in a way that gives product, but in the process, no additional reactants are consumed and no additional products are made. It takes the general form of 
Substitution reactions are ones in which there is some sort of exchange of atoms or functional groups between different reactants to give new products. In the reaction shown in the question stem, this qualifies as a substitution reaction.
Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources