All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
For Constant Temperature, Gibbs Free Energy is defined as:
Where , 



Which of the following scenarios is not possible?
The following condition is not possible:
This is because if enthalpy is positive, and entropy is negative, the negative sign in front of the temperature term in the formula becomes positive. Addition of 2 positive numbers can not be negative. Plugging in arbitrary numbers into the other conditions can show they are all possible.
Take the following condition:

Then Gibbs free energy 

Example Question #1 : Thermodynamics
For constant temperature, Gibbs free energy is defined as:
Where , 


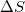
Given that a system is spontaneous, which of the following states are possible?
I.
II.
III.
IV.
IV only
I, II, III, and IV
I and III
II and III
I, II, and III
I and III
Condition I is always true. Condition II is never true, as Gibbs free energy cannot be negative if enthalpy is positive and entropy is negative. Condition III may be true if temperature is very high (this is the scenario when the 



Example Question #3 : Thermochemistry And Thermodynamics
The enthalpy of a reaction is 


Cannot be determined from the given information
Cannot be determined from the given information
Gibbs free energy of a system can be solved using the following equation.
where 




Example Question #1 : Gibbs Free Energy
In an exergonic reaction, products will have __________ Gibbs free energy and the reaction is __________.
lower . . . nonspontaneous
lower . . . spontaneous
higher . . . nonspontaneous
higher . . . spontaneous
lower . . . spontaneous
Exergonic reaction suggests that the Gibbs free energy is negative. Since the change in Gibbs free energy is defined as Gibbs free energy of products - Gibbs free energy of reactants, a negative change in Gibbs free energy suggests that the products have a lower Gibbs free energy than reactants. A reaction is spontaneous if it has negative Gibbs free energy; therefore, exergonic reactions are always spontaneous. This is because the reaction is producing a more stable product (lower energy) from a less stable reactant (higher energy).
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All Physical Chemistry Resources




















