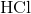All SAT II Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Molecules
Based on VSEPR theory and electron configurations, which of the following molecules is not matched with its correct geometry?




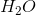


Example Question #4 : Sat Subject Test In Chemistry
What is the molecular geometry of 
Square planar
Octahedral
Square pyramidal
Tetrahedral
Trigonal pyramidal
Square pyramidal
There are six electron domains in 


Example Question #1 : Naming Compounds
Which of the following is the correct name of 
Dinitrogen tetraoxide
Nitrogen monoxide
Dinitrogen monoxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Dinitrogen pentoxide
Dinitrogen tetraoxide
In order to answer the question, it is important to first determine what kind of bonding is occurring in order to properly name the molecule. When nitrogen and oxygen form an 
Because a covalent bond is formed, we can determine that name of the molecule will be based on number of each atom in the molecule. There are two nitrogen atoms in the resulting molecule, so the prefix in front of the "nitrogen" part of the name will be "di-," meaning two. There are four oxygen atoms in the resulting molecule, so the prefix in front of the "oxygen" part of the name will be "tetra," meaning four.
The molecules names will be arranged alphabetically, and the second atom will have "-ide" as the suffix. Therefore, the correct answer is "dinitrogen tetroxide."
Example Question #4 : Sat Subject Test In Chemistry
What is the formula for the compound formed from calcium and sulfate ions?
In order to answer this question correctly, it is important to have knowledge of the formation of ionic bonds, polyatomic ions, and the periodic table. First, it is important to notice that calcium ions and sulfate ions will form an ionic bond. Knowing this, it can be understood that valance electrons will be exchanged between the ions and therefore, oppositely charged ions that are attracted to each other will be formed.
Calcium is in the second column of the periodic table, so it will provide two ions to the sulfate polyatomic ion. This will form a calcium cation (

One calcium ion provides two electrons, which are both accepted by a sulfate polyatomic ion, so the ratio of calcium ions used to sulfate polyatomic ions used is 1:1. This means that only one of each ion is needed to form the compound, making the formula 
Initially it may be tempting to write the formula as 
Example Question #5 : Sat Subject Test In Chemistry
All of the following are properties of zinc. Which of the following are chemical properties of zinc?
A. Zinc produces hydrogen gas when placed in acid.
B. Zinc melts at 
C. The density of zinc is 
D. Zinc is a grey metal.
E. Zinc corrodes in moist air.
B
C
B and C
A and E
A, C, and E
A and E
Physical properties are aspects of matter that can be observed and measured without changing it. Chemical properties measure the potential for undergoing a chemical change. How zinc reacts to acid and in moist air are both chemical properties because the zinc is undergoing chemical change in each environment. The color, density, and melting point of the zinc can all be observed without changing the nature of the matter, so these are physical properties of zinc.
Example Question #11 : Sat Subject Test In Chemistry
Which of the following are strong electrolytes?
All five
One
Two
Three
Four
Three
Strong electrolytes are substances that exists in solutions as only ions. These substances dissociate 100% in solutions. Strong acids, strong bases, and salts are all examples of strong electrolytes. 




Example Question #1 : Compounds And Molecules
How many of the following compounds are ionic?
Zero
All five
Two
Three
One
Two
Ionic compounds are chemical compounds made of charged ions held together by forces called ionic bonding. Ionic bonds are formed by transfers of valance electrons, which create charged atoms (ions) which are attracted to each other because they have opposite charges. This is not be confused with covalent bonding, in which atoms form an attraction by sharing electrons.


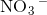



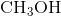




Example Question #1 : Hydrogen Bonding
Which of the following does not exhibit hydrogen bonding as an intermolecular force?
Hydrogen bonding occurs between hydrogen and a very electronegative atom, which is usually fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen. Thus, hydrogen bonding does not occur in 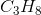
Example Question #1 : Intermolecular Forces
In a solution, a weak electrolyte exists predominately as which of the following?
Molecules
Ions
Isotopes
Polyatomic ions
Electrons
Molecules
An electrolyte is a substance that when dissolved in a solution breaks up into ions. More specifically, an electrolyte breaks up into cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). While strong electrolytes break up 100% into anions and cations, weak electrolytes break apart significantly less. Less than 10% of a weak electrolyte ionizes at all in solution. That means the 90%–99% of the weak electrolyte's molecules do not ionize. This is because the intermolecular forces that form between the solution and the weak electrolyte's molecules are not stronger than the intramolecular forces holding the molecule together. While solutions containing weak electrolytes contain both ions formed from the weak electrolyte ions and molecules of the weak electrolyte, they contain mostly molecules of the weak electrolyte.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All SAT II Chemistry Resources