All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #14 : Acute / Obtuse Isosceles Triangles
A triangle has a perimeter of 


The answer is 
Since we know that the permieter is 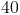


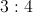





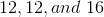

Example Question #231 : Plane Geometry
In the standard 


To form an isosceles triangle here, we need to create a third vertex whose 






Example Question #232 : Plane Geometry

Note: Figure is not drawn to scale.
In the figure above, points 






Because 



We know that 




Example Question #233 : Plane Geometry
A light beam of pure white light is aimed horizontally at a prism, which splits the light into two streams that diverge at a 

What is the distance, in feet, between the two sensors?
Round your final answer to the nearest tenth. Do not round until then.
This problem can be solved when one realizes that the light beam's split has resulted in an acute isosceles triangle. The triangle as stated has two sides of 




Since we know at least two angles and at least one side of our triangle, we can use the Law of Sines to calculate the remainder. The Law of Sines says that for any triangle with angles 




Plugging in one of our 


Next, cross-multiply:

Now simplify and solve:
Rounding, we see our missing side is 
Certified Tutor
All ACT Math Resources




























