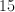All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #413 : Hspt Mathematics
Two angles are supplementary and have a ratio of 1:4. What is the size of the smaller angle?
Since the angles are supplementary, their sum is 180 degrees. Because they are in a ratio of 1:4, the following expression could be written:
Example Question #1 : Plane Geometry

AB and CD are two parrellel lines intersected by line EF. If the measure of angle 1 is 
The angles are equal. When two parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, the corresponding angles have the same measure.
Example Question #1 : Intersecting Lines And Angles
Figure not drawn to scale.
In the figure above, APB forms a straight line. If the measure of angle APC is eighty-one degrees larger than the measure of angle DPB, and the measures of angles CPD and DPB are equal, then what is the measure, in degrees, of angle CPB?
33
40
50
66
114
66
Let x equal the measure of angle DPB. Because the measure of angle APC is eighty-one degrees larger than the measure of DPB, we can represent this angle's measure as x + 81. Also, because the measure of angle CPD is equal to the measure of angle DPB, we can represent the measure of CPD as x.
Since APB is a straight line, the sum of the measures of angles DPB, APC, and CPD must all equal 180; therefore, we can write the following equation to find x:
x + (x + 81) + x = 180
Simplify by collecting the x terms.
3x + 81 = 180
Subtract 81 from both sides.
3x = 99
Divide by 3.
x = 33.
This means that the measures of angles DPB and CPD are both equal to 33 degrees. The original question asks us to find the measure of angle CPB, which is equal to the sum of the measures of angles DPB and CPD.
measure of CPB = 33 + 33 = 66.
The answer is 66.
Example Question #2 : Plane Geometry
One-half of the measure of the supplement of angle ABC is equal to the twice the measure of angle ABC. What is the measure, in degrees, of the complement of angle ABC?
36
72
18
90
54
54
Let x equal the measure of angle ABC, let y equal the measure of the supplement of angle ABC, and let z equal the measure of the complement of angle ABC.
Because x and y are supplements, the sum of their measures must equal 180. In other words, x + y = 180.
We are told that one-half of the measure of the supplement is equal to twice the measure of ABC. We could write this equation as follows:
(1/2)y = 2x.
Because x + y = 180, we can solve for y in terms of x by subtracting x from both sides. In other words, y = 180 – x. Next, we can substitute this value into the equation (1/2)y = 2x and then solve for x.
(1/2)(180-x) = 2x.
Multiply both sides by 2 to get rid of the fraction.
(180 – x) = 4x.
Add x to both sides.
180 = 5x.
Divide both sides by 5.
x = 36.
The measure of angle ABC is 36 degrees. However, the original question asks us to find the measure of the complement of ABC, which we denoted previously as z. Because the sum of the measure of an angle and the measure of its complement equals 90, we can write the following equation:
x + z = 90.
Now, we can substitute 36 as the value of x and then solve for z.
36 + z = 90.
Subtract 36 from both sides.
z = 54.
The answer is 54.
Example Question #1 : Plane Geometry

In the diagram, AB || CD. What is the value of a+b?
60°
160°
80°
None of the other answers.
140°
160°
Refer to the following diagram while reading the explanation:

We know that angle b has to be equal to its vertical angle (the angle directly "across" the intersection). Therefore, it is 20°.
Furthermore, given the properties of parallel lines, we know that the supplementary angle to a must be 40°. Based on the rule for supplements, we know that a + 40° = 180°. Solving for a, we get a = 140°.
Therefore, a + b = 140° + 20° = 160°
Example Question #1 : Lines
In rectangle ABCD, both diagonals are drawn and intersect at point E.
Let the measure of angle AEB equal x degrees.
Let the measure of angle BEC equal y degrees.
Let the measure of angle CED equal z degrees.
Find the measure of angle AED in terms of x, y, and/or z.
180 – 1/2(x + z)
360 – x + y + z
180 – (x + y + z)
180 – 2(x + z)
180 – y
180 – 1/2(x + z)
Intersecting lines create two pairs of vertical angles which are congruent. Therefore, we can deduce that y = measure of angle AED.
Furthermore, intersecting lines create adjacent angles that are supplementary (sum to 180 degrees). Therefore, we can deduce that x + y + z + (measure of angle AED) = 360.
Substituting the first equation into the second equation, we get
x + (measure of angle AED) + z + (measure of angle AED) = 360
2(measure of angle AED) + x + z = 360
2(measure of angle AED) = 360 – (x + z)
Divide by two and get:
measure of angle AED = 180 – 1/2(x + z)
Example Question #2021 : Hspt Mathematics
A student creates a challenge for his friend. He first draws a square, the adds the line for each of the 2 diagonals. Finally, he asks his friend to draw the circle that has the most intersections possible.
How many intersections will this circle have?

Example Question #1 : Geometry
Two pairs of parallel lines intersect:

If A = 135o, what is 2*|B-C| = ?
180°
150°
140°
170°
160°
180°
By properties of parallel lines A+B = 180o, B = 45o, C = A = 135o, so 2*|B-C| = 2* |45-135| = 180o
Example Question #1 : Geometry
Lines 





Not enough information.
Since we know opposite angles are equal, it follows that angle 

Imagine a parallel line passing through point 




Example Question #1 : Geometry
If 


When the measure of an angle is added to the measure of its supplement, the result is always 180 degrees. Put differently, two angles are said to be supplementary if the sum of their measures is 180 degrees. For example, two angles whose measures are 50 degrees and 130 degrees are supplementary, because the sum of 50 and 130 degrees is 180 degrees. We can thus write the following equation:
Subtract 40 from both sides.
Add 
The answer is 
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ACT Math Resources