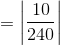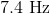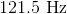All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
The literature value for the melting point of a given compound is 240 degrees Celsius. A scientist uses the melting point apparatus to experimentally measure the compound's melting point at 230 degrees Celsius. What is the scientist's percent error?
The percent error is given by the following formula:

In this case, the theoretical value is 240 degrees Celsius, and the actual value is 230 degrees Celsius. The percent error is thus calculated to be 4.16 %. The calculation is as follows:
Example Question #1 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
A scientist wants to separate and purify a small, positively charged protein. Which of the following techniques might be employed to accomplish this task?
Thin layer chromatography
Size exclusion chromatography and cation exchange chromatography
Reverse phase chromatography
Normal phase chromatography
None of these
Size exclusion chromatography and cation exchange chromatography
Size exclusion chromatography is a good technique for separating proteins based on size due to tiny pores in the beads in the column (the smaller proteins will elute out last). Cation exchange chromatography is a good technique for separating proteins based on charge due to negatively charged beads in the column (the positively charged molecules will elute out last). Normal and reverse phase chromatography are methods of separation based on a molecule's polarity; in normal phase chromatography, a nonpolar mobile phase is employed so that polar, hydrophilic molecules elute last. The opposite is true for reverse phase chromatography - a polar, aqueous mobile phase is used and any nonpolar molecules tend to adsorb to the hydrophobic beads, causing them to elute out last. Thin layer chromatography is not a good method of purifying substances, rather, it is a better indicator of reaction progress via elucidation of the retardation factor, 
Example Question #1 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
In reverse phase chromatography, the more __________ molecules will be eluted __________.
hydrophobic . . . first
hydrophilic . . . last
More than one of these
hydrophobic . . . last
None of these answers
hydrophobic . . . last
In reverse phase chromatography, the more hydrophobic molecules will be eluted last (the more hydrophilic molecules will be eluted first). This is due to the mobile phase being polar, and thus the nonpolar/hydrophobic molecules adsorbing to the stationary phase. The opposite is true in normal phase chromatography - this technique employs a nonpolar mobile phase and a polar stationary phase. The polar stationary phase will attract polar molecules, and thus the nonpolar molecules will be eluted first along with the nonpolar/hydrophobic mobile phase.
Example Question #2 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
Which choice of lab equipment is never used to make accurate volume measurements?
Burette
Volumetric flask
Beaker
Graduated cylinder
Beaker
Graduated cylinders are often used for measuring volumetric quantities. As these have several markings, they are considered accurate. Volumetric flasks are also used to accurately measure liquid volume quantities. Lastly, burettes are used to accurately measure volumes of liquid during titrations.
In contrast, beakers are not typically used to measure accurate quantities of liquid; though they have markings on them, these are approximate measurements. Graduated cylinders are often used to accurately measure out a liquid, and beakers to then hold the liquid.
Example Question #3 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
Which of the following techniques could be used to separate a mixture of solvents based on their boiling points?
Infrared spectroscopy
Distillation
Thin layer chromatography
Column chromatography
Crystallization
Distillation
The process of distillation is used to separate a mixture of volatile liquids by their boiling points. This is done by heating a mixture of liquids, condensing whatever gets evaporated, and then filtering out the individual components one by one. Crystallization is a time intensive purification process that allows for the formation of a compound's crystals, and separates molecules based on solubility. Thin layer chromatography is a quick technique used to analyze non-volatile mixtures and is performed on a sheet of silica (which acts as the stationary phase). Column chromatography is another purification method used to separate the components of mixture. Infrared spectroscopy is an analyzation technique, not a separation technique.
Example Question #181 : College Chemistry
The flame test relates most closely to which of the following phenomena in quantum mechanics?
Mass defect effect
Photoelectric effect
Electron shielding effect
Relativity
The effects of Van der Waals forces
Photoelectric effect
Both the photoelectric effect and the flame test display the effects of excited electrons releasing energy as they move from higher to lower quantum levels. The mass defect effect refers to the energy input needed to create the strong nuclear force, which binds the nucleus of an atom together. Electron shielding is an effect that relates to bonding and effective nuclear charge. Van der Waals forces are weak molecular forces that do not relate to energy releases exhibited by the flame test. Relativity is a phenomenon in physics relating to the space and time of two objects and their motion relative to each other.
Example Question #6 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
What is the frequency of a photon with a wavelength of 
To solve this problem we need to use the following equation:
Where, 




First, convert the 

Now we can plug the wavelength and the speed of light into the equation above and solve for frequency.
Example Question #1 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
What is the wavelength of a photon with a frequency of 
To solve this problem we need to use the following equation:
Where 






The frequency given in the problem and the speed of light can be plugged into the equation above to solve for wavelength.
Example Question #8 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
What is the wavelength of a radio wave with the frequency 
To solve this problem we need to use the following equation:
where,







First, convert the 
Now we can plug the wavelength and the speed of light into the equation above and solve for frequency.
Example Question #1 : Laboratory Techniques And Analysis
Which of the following procedures would be most effective for separating a homogenous mixture of two liquids that have significantly different boiling points?
Distillation
Centrifugation
Electrophoresis
Chromatography
Distillation
In this question, we're asked to identify a laboratory procedure that is best suited for separating two liquids of different boiling points in a mixture.
Let's go through each of the procedures listed in the answer choices to see what they do.
Chromatography is a procedure used to separate mixtures based on the fact that different molecules will adhere differently, depending on the type of chromatography used. For instance, ion-exchange chromatography is a technique often employed in biochemistry in order to separate positively or negatively charged peptides from a larger sample. However, chromatography would not be the best technique to separate two liquids that make up a homogenous mixture.
Centrifugation is a technique used to separate bulk particles from one another in a solution. As a result of spinning the sample at extremely high speeds, the tremendous centripetal force causes the particles to sediment at different rates due to differences in their physical properties such as size, shape, and weight. As an example, healthcare professionals can centrifuge a patient's blood in order to determine the various proportions of red blood cells among other things. This gives them information that can help them diagnose illnesses in the patient. However, centrifugation would not be an appropriate technique to separate two liquids in a homogenous mixture.
Electrophoresis is another separation technique. A sample is added to a plate containing a thick gel such as agarose. The two ends of the plate are oppositely charged, with a resulting electric field between the ends. This setup allows for the sample to travel through the agarose gel from one end towards the other. Due to differences in size and shape of the sample, different compounds will travel through the thick gel at different rates. This technique is often useful in biochemistry, for example, where scientists can separate proteins or nucleic acids to provide them with a wealth of information. This technique, however, would not prove useful for separating liquids.
Distillation is the answer we are looking for. It is a technique used to separate a mixture of two liquids due to differences in boiling point. In this technique, enough heat is added to the mixture in order to bring the temperature to the boiling point of the compound that has a lower boiling point. As a result, the liquid with the lower boiling point will boil, while the other liquid will remain as a liquid. The gas given off by boiling is collected in another container and condensed back into the liquid state. Some variations on distillation allow for more efficient separation. For example, fractional distillation is a process that allows for the separation of two liquids that have boiling points closer to one another. In the fractional version, the gas given off by the boiling liquid ascends through a column. As the gas rises, some of it condenses on the column. This condensed liquid contains some of both liquids still, but it has a relatively larger percentage of the liquid with the lower boiling point. However, this small amount of liquid will then re-boil, turning into gas. This process keeps repeating itself, but due to even a small difference in boiling points, the gas that is given off each time will contain a progressively larger proportion of the liquid that has a lower boiling point. Thus, fractional distillation has the potential to be much more efficient than simple distillation.
Certified Tutor
All College Chemistry Resources