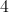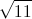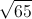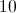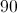All Common Core: 8th Grade Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Apply The Pythagorean Theorem To Determine Unknown Side Lengths In Right Triangles: Ccss.Math.Content.8.G.B.7
The base and height of a right triangle are each 1 inch. What is the hypotenuse?
You need to use the Pythagorean Theorem, which is 
Add the first two values and you get 

Example Question #412 : Grade 8
A right triangle has legs with lengths of 






Using the numbers given to us by the question,

Example Question #471 : Geometry
A right triangle has legs with the lengths 

Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Example Question #2 : Apply The Pythagorean Theorem To Determine Unknown Side Lengths In Right Triangles: Ccss.Math.Content.8.G.B.7
Find the length of the hypotenuse in the right triangle below.

Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse.
Example Question #101 : Geometry
If a right triangle has a base of 

To solve this problem, we must utilize the Pythagorean Theorom, which states that:
We know that the base is 





Next we evaluate the exponents:
Now we add them together:
Then, 


Example Question #101 : Geometry
If a right triangle has a base of 

To solve this problem, we are going to use the Pythagorean Theorom, which states that 
We know that this particular right triangle has a base of 



Next, we evaluate the expoenents:
Then, 
To solve for 


Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
What is the hypotenuse of a right triangle with sides 5 and 8?
undefined
According to the Pythagorean Theorem, the equation for the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 



Example Question #3 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
In a right triangle, two sides have length 

By the Pythagorean Theorem, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Let 

Example Question #1 : Apply The Pythagorean Theorem To Determine Unknown Side Lengths In Right Triangles: Ccss.Math.Content.8.G.B.7
In a right triangle, two sides have lengths 5 centimeters and 12 centimeters. Give the length of the hypotenuse.
This triangle has two angles of 45 and 90 degrees, so the third angle must measure 45 degrees; this is therefore an isosceles right triangle.
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Let 


Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Hypotenuse Of A Right Triangle : Pythagorean Theorem
In a right triangle, the legs are 7 feet long and 12 feet long. How long is the hypotenuse?
The pythagorean theory should be used to solve this problem.
Certified Tutor
All Common Core: 8th Grade Math Resources