All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Circles
What is the circumference of a circle with an area of 36π?
None of the other answers
6π
32
12π
15π
12π
We know that the area of a circle can be expressed: a = πr2
If we know that the area is 36π, we can substitute this into said equation and get: 36π = πr2
Solving for r, we get: 36 = r2; (after taking the square root of both sides:) 6 = r
Now, we know that the circuference of a circle is expressed: c = πd. Since we know that d = 2r (two radii, placed one after the other, make a diameter), we can rewrite the circumference equation to be: c = 2πr
Since we have r, we can rewrite this to be: c = 2π*6 = 12π
Example Question #1 : Geometry
Which is greater: the circumference of a circle with an area of 

The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
The circumference of the circle is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
The perimeter of the square is greater.
The circumference of the circle is greater.
Starting with the circle, we need to find the radius in order to get the circumference. Find 
Then calculate circumference:


To find the perimeter of the square, we can use 



Example Question #1 : Plane Geometry
Circle A has an area of 
Based on our information, we know that the 121π = πr2; 121 = r2; r = 11.
Our other circle with half the radius of A has a diameter equal to the radius of A. Therefore, the circumference of this circle is 11π. Half of this is 5.5π. However, since this is a semi circle, it is enclosed and looks like this:
Therefore, we have to include the diameter in the perimeter. Therefore, the total perimeter of the semi-circle is 5.5π + 11.
Example Question #2 : Geometry
Quantity A: The circumference of a circle with radius
Quantity B: The area of a circle with a diameter one fourth the radius of the circle in Quantity A
Which of the following is true?
The relationship between the two values cannot be determined.
Quantity A is larger.
Quantity B is larger.
The two quantities are equal.
The relationship between the two values cannot be determined.
Let's compute each value separately. We know that the radii are positive numbers that are greater than or equal to 

Quantity A
Since 
Quantity B
If the diameter is one-fourth the radius of A, we know:
Thus, the radius must be half of that, or 
Now, we need to compute the area of this circle. We know:
Therefore,
Now, notice that if 
However, if we choose a value like 
Quantity A:
Quantity B:
Therefore, the relation cannot be determined!
Example Question #7 : Circles

Circle 

The area of Square 


What is the circumference of Circle 






Since we know that the area of Square 











The circumference of this circle is defined as:

(You could also compute this from the diameter, but many students just memorize the formula above.)
Example Question #2 : Circles
What is the area of a circle, one-quarter of the circumference of which is 5.5 inches?
121/π
121π
π/3
225π
121/π
Here, you need to “solve backward” from the data you have been given. We know that 0.25C = 5.5; therefore, C = 22. In order to solve for the area, we will need the radius of the circle. This can be obtained by recalling that C = 2πr. Replacing 22 for C, we get 22 = 2πr.
Solve for r: r = 22 / 2π = 11 / π.
Now, we solve for the area: A = πr2. Replacing 11 / π for r: A = π (11 / π)2 = (121π) / (π2) = 121 / π.
Example Question #3 : Geometry
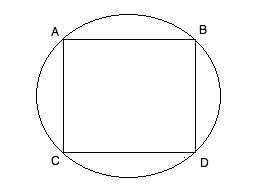
In the diagram above, square ABCD is inscribed in the circle. If the area of the square is 9, what is the area of the circle?
9π
18π
4.5π
3π
3√(2)π
4.5π
If the area of the square is 9, then s2 = 9 and s = 3. If the sides thus equal 3, we can calculate the diagonals (either CB or AD) by using the 45-45-90 triangle ratio. For a side of 3, the diagonal will be 3√(2). Note that since the square is inscribed in the circle, this diagonal is also the diameter of the circle. If it is such, the radius is one half of that or 1.5√(2).
Based on that value, we can computer the circle’s area:
A = πr2 = π(1.5√(2))2 = (2.25 * 2)π = 4.5π
Example Question #1 : Circles
Quantitative Comparison
Quantity A: Area of a circle with radius r
Quantity B: Perimeter of a circle with radius r
Quantity B is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity A is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Try different values for the radius to see if a pattern emerges. The formulas needed are Area = πr2 and Perimeter = 2πr.
If r = 1, then the Area = π and the Perimeter = 2π, so the perimeter is larger.
If r = 4, then the area = 16π and the perimeter = 8π, so the area is larger.
Therefore the relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Example Question #11 : Plane Geometry
Quantitative Comparison
A circle has a radius of 2.
Quantity A: The area of the circle
Quantity B: The circumference of the circle
Quantity A is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
The two quantities are equal.
This is one of the only special cases where the area equals the circumference of the circle. The Area = πr2 = 4π. The circumference = 2πr = 4π.
Note: For a quantitative comparison such as this one where the columns have numeric values instead of variables, the answer will rarely be "cannot be determined".
Example Question #1 : Radius
Quantitative Comparison
Quantity A: Area of a right triangle with sides 7, 24, 25
Quantity B: Area of a circle with radius 5
The two quantities are equal.
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Quantity B is greater.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity A: area = base * height / 2 = 7 * 24/2 = 84
Quantity B: area = πr2 = 25π
Now we have to remember what π is. Using π = 3, the area is approximately 75. Using π = 3.14, the area increases a little bit, but no matter how exact an approximation for π, this area will never be larger than Quantity A.
All GRE Math Resources