All GRE Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #31 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
Quantitative Comparison: Compare Quantity A and Quantity B, using additional information centered above the two quantities if such information is given.
Quantity A Quantity B
43 34
The answer cannot be determined from the information given.
Quantity B is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
In order to determine the relationship between the quantities, solve each quantity.
43 is 4 * 4 * 4 = 64
34 is 3 * 3 * 3 * 3 = 81
Therefore, Quantity B is greater.
Example Question #32 : Gre Quantitative Reasoning
Quantity A:
Quantity B:
The relationship cannot be determined from the information given.
Quantity A is greater.
Quantity B is greater.
The two quantities are equal.
Quantity B is greater.
(–1) 137= –1
–1 < 0
(–1) odd # always equals –1.
(–1) even # always equals +1.
Example Question #34 : Exponents
Anything raised to negative power means 
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Rational Number From An Exponent
Which of the following is not the same as the others?
Let's all convert the bases to 

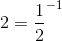
Therefore,

Example Question #41 : Algebra
Simplify
Whenever you see lots of multiplication (e.g. exponents, which are notation for repetitive multiplication) separated by addition or subtraction, a common way to transform the expression is to factor out common terms on either side of the + or - sign. That allows you to create more multiplication, which is helpful in reducing fractions or in reducing the addition/subtraction to numbers you can quickly calculate by hand as you'll see here.
So let's factor a 
We have 
And you'll see that the addition inside parentheses becomes quite manageable, leading to the final answer of 
All GRE Math Resources















![4^{12}=[2^2]^{12}=2^{24}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/340115/gif.latex)

![16^8=[2^4]^8=2^{32}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/340117/gif.latex)
![\left(\left[\frac{1}{2}\right]^{-24}\right)^{-1}=2^{24}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/342256/gif.latex)










