All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1503 : Mcat Biological Sciences
The molecules shown below are best described as __________.
enantiomers
diastereomers
epimers
isomers
isomers
The molecules in this problem are isomers because they each have unique configurations and do not share the same funcitonal groups at the same carbon positions. Enantiomers are reflections of each other. Diastereomers are stereoisomers that differ at one or more stereocenters, while epimers are stereoisomers that differ at only one stereocenter.
Example Question #1 : Isomers
Which of the following is not a geometric isomer of pentene?


All of these are geometric isomers of pentene.



Geometric isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but they differ in the way they are arranged spatially. Pentene carries the molecular formula, 

 and this compound is not a geometric isomer of pentene.
and this compound is not a geometric isomer of pentene.
Example Question #1 : Stereochemistry
A molecule has three chiral centers. How many stereoisomers of this compound will have different boiling points compared to the original molecule?
Seven
One
Six
Two
Six
The first step is to determine how many stereoisomers there are for this molecule. Since the number of stereoisomers is dependent on the number of chiral carbons, we can solve according to the equation 

Next, we need to compare the different stereoisomers to the original molecule. The original molecule will have one enantiomer and six diastereomers. Remember that enantiomers have the same physical properties, so we will not include this isomer in the final answer. Diastereomers, on the other hand, have different physical properties compared to the original molecule. As a result, six stereoisomers will have different boiling points compared to the original molecule.
Example Question #381 : Organic Chemistry
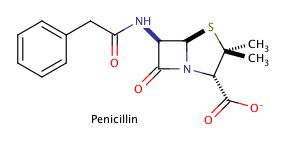
Shown above is the chemical structure for penicillin, a common prescription drug. How many chiral carbons does penicillin have?
Five
Two
Zero
Three
One
Three
The correct answer is three. The key to finding chiral carbons is to look for carbons that are attached to four different substituents. We can immediately eliminate any carbons that are involved in double bonds, or that have two hydrogens attached. Given this, we find that there are three chiral carbons. Note that carbon chains of varying content will qualify as different substituents, allowing chiral carbons to bond to two other carbons.
Example Question #2 : Stereochemistry
Compounds that are mirror images of each other are called __________.
conformers
enantiomers
stereoisomers
diastereomers
enantiomers
Stereoisomers are isomers that differ in the orientation of atoms in space, but have the same bonding patterns and structures. Enantiomers are a specific class of stereoisomers that differ in orientation around a chiral center to create mirror image molecules.
Diastereomers are a type of stereoisomer that are not related through a reflection operation, and may differ at more than one chiral center. Conformers have the same structural formula, but different shapes due to bond rotation.
Example Question #1 : Help With Epimers

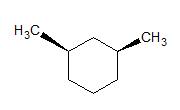
The given molecules are __________.
conformers
None of these
identical
constitutional isomers
stereoisomers
stereoisomers
Stereoisomers have different orientations around a single stereocenter. The two molecules are stereoisomers. Specifically, these molecules are epimers, meaning that they differ at only one stereocenter.
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula, but different structures. Conformers have different rotations around a single bond. The molecules are clearly not identical.
Example Question #61 : Isomers
Which of the following carbons represents the stereogenic center between the given isomers?


Carbon 5
Carbon 3
Carbon 1
Carbon 4
Carbon 2
Carbon 4
Epimers are isomers that have different configurations at only one carbon atom. This carbon atom is known as the stereogenic center. The given compounds are identical except for the orientation around carbon number 4; thus, carbon 4 is the stereogenic center.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Chemistry Resources