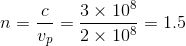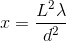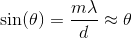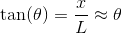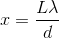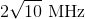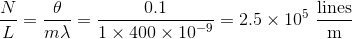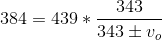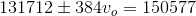All GRE Subject Test: Physics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #33 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A particle traveling through glass (index of refraction 1.33) emits Cherenkov radiation. Which of the following is a possible speed of the particle?
Cherenkov radiation is emitted by a particle traveling faster than the phase velocity of light in that medium. Because 
This is the minimum velocity of a particle to be emitting Cherenkov radiation in glass. This eliminates all answers except 


Example Question #34 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A monochromatic beam of 

The phase velocity of light through a medium with refractive index 
Solving this for 

Example Question #35 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A double slit experiment is set up with the following parameters: two slits are a separated by a distance 




The condition for constructive interference with double slit diffraction is given by:
Where 
Solving for the angle and using the small angle approximation, we get;
The distance 
Again, with the help of the small angle approximation. Setting the two thetas equal to each other and solving for 
For the central band, 


Example Question #36 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
Two waves with frequencies: 
The beat from two combined sound waves is:
Example Question #37 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A beam of light, with wavelength 

The equation describing maxima of a diffraction grating is:
Where d is the separation of slits, which can also be expressed as:
Substituting d into the first equation and making the small angle approximation, one can solve for 
Note that the angle had to be converted from degrees to radians. Finally, the question asks for lines per centimeter, not meter, so the answer becomes 
Example Question #41 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A car's horn has a frequency of 

The equation for the Doppler effect with frequency for a moving source is given by:
Where 



Example Question #1 : Electromagnetics, Waves, And Optics
A beam of unpolarized light passes through two linear polarizers whose polarization axes are at an angle theta with each other. The light initially has an intensity 


Initially unpolarized light passing though a linear polarizer decreases in intensity by a factor of two:
Malus's Law gives the change in intensity of polarized light passing through a linear polarizer in terms of the change in angle of polarization:
Combining the two equations, we get:
Solving for 
Example Question #42 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A beam of light travels through a medium with index of refraction 
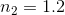
This situation is impossible.
Total internal reflection occurs at the angle:
However, this angle is measured from a line normal to the plane of the interface; the angle we want, therefore, is 

Example Question #43 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
The focal length of a thin convex lens is 



No image is created



Because the object is beyond 2 focal lengths of the lens, the image must be between 1 and 2 focal lengths on the opposite side. Therefore, the image must be between 
Alternatively, one can apply the thin lens equation:
Where 



Example Question #44 : Gre Subject Test: Physics
A candle 


No image is created.





First, find the image distance 
Magnification of a lens is given by:
Where 


Because the sign is negative, the image is inverted.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All GRE Subject Test: Physics Resources