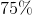All High School Physics Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Concept Of Energy Transfer
A microwave heats up a cold piece of pizza. What type of heat transfer is this?
Induction
There is no heat transfer
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
Radiation
Microwaves use radiation as the method of heat transfer. Radiation refers to heat transfer via electromagnetic waves, such as microwaves.
Conduction is heat transfer via direct contact between two objects. Convection is heat transfer via the movement of surrounding fluids. Induction is not a type of heat transfer.
Example Question #1 : Heat
A pot of water boils. What type of heat transfer occurs within the pot?
Convection
There is no heat transfer
Radiation
Conduction
Induction
Convection
Convection is heat transfer via the movement of surrounding fluids. Though conduction may be used to heat the pot, and in turn to heat the water molecules in contact with the edge of the pot, convection occurs inside the pot to transfer heat between the water molecules. This allows the water to heat evenly. Without convection occurring within the pot, the water at the outer edges would be much hotter than the water at the center.
Radiation refers to heat transfer via electromagnetic waves. Conduction is heat transfer via direct contact between two objects. Induction is not a type of heat transfer.
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Concept Of Energy Transfer
A piece of ice is placed on a hot surface and begins to melt, but its temperature does not increase. What type of heat transfer is this?
Convection
There is no heat transfer
Induction
Radiation
Conduction
Conduction
Heat is a form of energy, and can be used to alter the energy of chemical interactions. Ice, a solid, will be in a lower energy state than water, a liquid. The addition of heat energy allows for the increase in phase energy from solid to liquid. The energy addition is converted to a different form; thus, the temperature does not change. Conduction is heat transfer via direct contact between two objects, which describes the transfer between the hot surface and the ice.
Radiation refers to heat transfer via electromagnetic waves, such as microwaves. Convection is heat transfer via the movement of surrounding fluids. Induction is not a type of heat transfer.
Example Question #591 : High School Physics
A piece of tin sitting on a stove top becomes very hot. What type of heat transfer was involved?
Conduction
Convection
Induction
Radiation
There is no heat transfer
Conduction
Conduction is heat transfer via direct contact between two objects. As the piece of tin is in direct contact with the stove, heat can freely flow from the stove into the tin, causing it to become hotter.
Radiation refers to heat transfer via electromagnetic waves, such as microwaves. Convection is heat transfer via the movement of surrounding fluids. Induction is not a type of heat transfer.
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Concept Of Energy Transfer
On a cold day, the temperature often feels colder due to a wind chill. This is an example of what type of phenomenon?
Radiation
Conduction
Induction
Convection
None of these
Convection
On a cold day, the air temperature is less than your body temperature. As cold wind comes in contact with your body, heat is transferred from your body to the air moving past, making you colder. This type of heat transfer is known as convection, in which heat is transferred from an object (your body) to a fluid medium (the air).
Conduction is heat transfer due to direct contact between objects. Radiation is heat transfer due to electromagnetic waves. Induction is not a form of heat transfer.
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Concept Of Energy Transfer
A piece of bread is burned on one side and uncooked on the other after being heated in a toaster. What was the most likely form of heat transfer to cause the burn?
Radiation
Conduction
Convection
We need to know more information to reach a conclusion
Induction
Conduction
Conduction is a form of heat transfer requiring direct contact between two objects. In the question, the burned side of the bread was likely in direct contact with the heat source, while the other was only in contact with hot air. The burned side is heated by conduction, while the uncooked side is heated by convection.
Convection is the transfer of heat through a fluid medium, namely a liquid or gas. Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
Example Question #1 : Understanding The Concept Of Energy Transfer
Which of the following methods of heat transfer requires the two objects to be touching?
Convection
Radiation
Conduction
Induction
Thermodynamic discharge
Conduction
Conduction is the form of heat transfer that requires direct contact between two objects.
Radiation is heat transfer via electromagnetic radiation. Convection uses a fluid medium, such as air or water, for heat transfer. Induction and thermodynamic discharge are not recognized types of heat transfer.
Example Question #2 : Understanding The Concept Of Energy Transfer
A marshmallow on a stick is placed above a fire, but not touching the fire. The marshmallow heats up and softens. How is the marshmallow being heated?
I. Conduction
II. Convection
III. Radiation
I and II
I, II, and III
II and III
II only
III only
II and III
Conduction occurs when heat is transferred by direct contact between two objects. Convection occurs when heat is transferred via contact between a fluid and an object. Radiation is heat transfer via electromagnetic radiation.
In this question, the fire is a source of heat and electromagnetic radiation. When the radiation from the fire impacts the marshmallow, it is being heated by radiation. The fire is also heating the surrounding air, creating fluid currents. The heated air is also transferring energy to the marshmallow, heating by convection.
There is no conduction in this example.
Example Question #1 : Heat
A Carnot Cycle operates using a heat reservoir at a temperature of 


The efficiency of a Carnot Cycle is defined by:
In this calculation, temperatures are given in Kelvin. Since Celsius and Kelvin exist in a one-to-one ratio, a conversion is unnecessary unless desired. We will perform the conversion, since most classes will advise it.
Using these values, we can calculate the efficiency:
Convert this value to a percentage:
Example Question #1 : Understanding Heat And Temperature
The temperature of an ideal gas is raised from 


For this problem, use Gay-Lussac's law to set up a direct proportion between pressure and temperature. Note that this law only applies when volume is constant.
Plug in our given values and solve for the initial pressure.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All High School Physics Resources