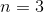All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Reactions By Product

What is the IUPAC name of the given diene?
5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene
3-chloro-2,5-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene
5-chloro-3,5-dimethyl-1,6-heptadiene
None of these answers
3-chloro-2,5-dimethyl-2,6-heptadiene
5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene
You must begin counting the carbons so that the first functional substituent has the lowest possible number. In this case, C1 is connected to C2 by the double bond, meaning we start counting from the left.
The longest carbon chain is seven carbons so the parent molecule is heptane. With this numbering, there are methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6 and a chlorine on carbon 5.
Substituents are named in alphabetical order and two double bonds result in a diene. Thus, the correct answer is 5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene.
Example Question #2 : Help With Alkene Synthesis

What is the value of 
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.
Example Question #1 : Reactions By Product
Which of the following reagents would convert butanone into 2-butene?
1.
2. Heat/
1.
2.
1.
2. Heat/
1.
2. Heat/
Two sets of reagents are required to convert butanone into 2-butene. First, we use 
1. 

Example Question #601 : Organic Chemistry
2-butone is reacted with 

Butane
None of these
2-butanol
2-butene
2-butene
2-butone is a carbonyl compound that can readily be reduced by 
Example Question #9 : Hydrocarbon Products

What is the reactant of the given reaction?

![]()




This is an addition reaction with 3 products. The unknown reactant reacts with 

Example Question #2 : Reactions By Product
Which of the following reagents can be used to create a E alkene from an alkyne?
None of these
Metallic sodium in liquid ammonia creates solvated electrons which can convert an alkyne to an E alkene. The same will not happen when sodium is combined with water, where sodium reacts violently to create sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Lindlar's catalyst is a poisoned catalyst used to form alkenes from alkynes, bud results in a Z conformation. Without the poisoned catalyst, an alkane will be formed.
Example Question #3 : Help With Alkene Synthesis

What is the major product for the reaction given?





The reason this is the major product is because on tertiary alcohols are best dehydrated based on the E1 mechanism below:

Example Question #601 : Organic Chemistry

What is the major product for the reaction given?





The reason this is the major product is because tertiary alcohols are best dehydrated based on the E1 mechanism below:

Example Question #5 : Help With Alkene Synthesis

What is the major product for the reaction given?





Below is the mechanism for the reaction given to form the alkene:

Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources