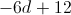All Pre-Algebra Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Distributive Property
Simplify the expression.
Use the distributive property to multiply each term of the polynomial by 
Example Question #1 : High School Math
Find the value of 
6
-6
4
2
-2
2
We can seperate the problem into two steps:
We then combine the two parts:
Example Question #2 : Distributive Property
Distribute 
When distributing with negative numbers we must remember to distribute the negative to all of the variables in the parentheses.
Distribute the 

Perform the multiplication remembering the positive/negative rules to get 
Example Question #3 : Distributive Property
Simplify the expression.
Multiply the mononomial by each term in the binomial, using the distributive property.
Example Question #2 : High School Math
Simplify the expression.
Use the distributive property to multiply each term by 
Simplify.
Example Question #4 : Distributive Property
Distribute:
When distributing with negative numbers we must remember to distribute the negative to all of the terms in the parentheses.
Remember, a negative multiplied by a negative is positive, and a negative multiplied by a positive number is negative.
Distribute the 
Perform the multiplication, remembering the positive/negative rules:
Example Question #5 : Distributive Property
Which of the following is equivalent to 
We need to distribute -3 by multiplying both terms inside the parentheses by -3.:

Now we can multiply and simplify. Remember that multiplying two negative numbers results in a positive number:
Example Question #6 : Distributive Property
Expand:
Use the distributive property. Do not forget that the negative sign needs to be distributed as well!
Add the terms together:
Example Question #7 : Distributive Property
Distribute:
Remember that a negative multiplied by a negative is positive, and a negative multiplied by a positive is negative.
Distribute the 
Example Question #8 : Distributive Property
Expand:
Distribute the 

and
Therefore, 5(2 + y) = 10 + 5y.
All Pre-Algebra Resources