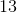All TACHS Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Geometry
A square has perimeter 24 feet. Give its area.
576 square feet
144 square feet
36 square feet
18 square feet
36 square feet
The perimeter of a figure is the sum of the lengths of its sides. A square comprises four sides of equal length, so, if the perimeter of the square is 24 feet, then each side has length

The area of the square is equal to the length of a side multiplied by itself, so the area of this square is

Example Question #32 : Tachs: Math And Ability
Jennifer wants to wallpaper her room which is made up for four rectangular walls each measuring at 


Start by finding out the total square footage of wallpaper needed.
Find the area of one wall. Recall that in order to find the area of a rectangle, you must multiply the length by the width.
Since we have four identical walls,
Now divide this by the amount of square feet covered by each roll of wallpaper to find how many rolls are needed.
Example Question #31 : Tachs: Math And Ability
Find the area of a circle with the following radius:
The area of a circle can be calculated using the following formula:
In this formula the radius is denoted by the variable, 
Substitute in the known variables and solve for the circle's area.
Example Question #3 : Area
Which is equal to the radius of a circle with area
The formula for the area 




To find the radius 

Now, find the square root of both sides. Since 

The radius of the given circle is 20.
Example Question #2 : Geometry
To determine whether a machine on an assembly line is filling bottles with the correct amount of soda, twenty bottles are selected. The tenth bottle and every tenth bottle after that are taken off the line and examined.
This is an example of which kind of sampling?
Systematic sampling
Stratified sampling
Cluster sampling
Convenience sampling
Systematic sampling
The sample in this scenario is selected from the population by choosing obects that occur at regular intervals. That makes this an example of systematic sampling.
Example Question #2 : Geometry
What is the area of a circle that has a diameter of 
Recall how to find the area of a circle:
To find the length of the radius, divide the diameter by two.
Now, plug it into the equation for the area of a circle.
Certified Tutor
All TACHS Math Resources