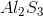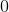All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Molecules And Compounds
In an ionic bond, electrons are __________.
destroyed
transferred
repelled
shared
excited
transferred
In an ionic bond, electrons are transferred to make a compound. For example, a sodium atom and a chloride atom can combine, exchanging electrons to form: 
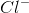

Example Question #2 : Introductory Topics
Which of these can be formed when ionic bonds break down?
Micelle
None of these; ionic bonds never break down.
Lattice structure
Cation
Cation
Ionic bonds are bonds involving the attraction between oppositely-charged ions. An example of an ionic compound is 


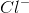
Ionic compounds have a characteristic lattice structure--that is, the arrangement of ions in a regular, geometric pattern. In the case of 



Lastly, micelles are lipid molecules which, in aqueous solution, arrange themselves in a spherical form. This is a response to the fact that fatty acids have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions (they are amphipathic). It has nothing to do with ionic bonds.
Example Question #1 : Introductory Topics
What is the molecular formula for aluminum sulfide?
Sulfur is much more electronegative than Aluminum (a metal), so when they bond they form an ionic compound as Aluminum transfers its electrons to Sulfur. Aluminum has a valence of 3, meaning that each Aluminum atom is looking to share or transfer 3 electrons to achieve a stable configuration. Sulfur has a valence of 6, meaning that each Sulfur atom is looking for two electrons to complete its octet. Thus, two Aluminum atoms will bond with three Sulfur atoms, resulting in the transfer of six electrons in total.
Example Question #1 : Ionic Bonds
What is the charge on the cation in the ionic compound sodium oxide?
When sodium and oxygen form the ionic compound sodium oxide, 
Example Question #1 : Covalent Bonds
Which of the following is a characteristic of covalent bonds?
A covalent bond is one between a metal and a nonmetal.
Covalent compounds dissolve in water to form cations and anions.
A covalent bond is one between two nonmetals.
Covalent compounds are good conductors of electricity.
A covalent bond is one between two nonmetals.
A covalent bond is one between two nonmetals, while an ionic bond is formed between a metal and a nonmetal. Covalent bonds also do not dissociate in aqueous solution to form cations and anions; this is a characteristic of ionic bonds. For example, 





Example Question #2 : Covalent Bonds
Which of the following is an example of a nonpolar covalent bond?
A covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals, in which electrons are shared. This means that 

A polar covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals in which one nonmetal is more electronegative than the other, pulling the shared electrons toward itself. This occurs in 

A nonpolar covalent bond is a bond between two nonmetals in which electrons are shared equally between the nonmetals. This occurs when the two nonmetals are of equal electronegativity. As the atoms of 
Example Question #1 : Molecules And Compounds
Which of the following compounds contains 
For this question, we're asked to determine which answer choice represents a compound with a total of six covalent bonds.
To answer this, we'll need to know the structure of each of the compounds. Moreover, it's important to remember that double bonds count as two covalent bonds.
Both sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid have a total of eight covalent bonds, while nitric acid has five. Carbonic acid is the only one shown that contains six covalent bonds, making it the correct answer.
Example Question #1 : Molecules And Compounds
Which of the following lists bond strength in order of weakest to strongest?
Hydrogen, dipole-dipole, ionic, covalent
Covalent, ionic, hydrogen, dipole-dipole
Dipole-dipole, covalent, hydrogen, ionic
Dipole-dipole, ionic, hydrogen, covalent
Dipole-dipole, hydrogen, covalent, ionic
Dipole-dipole, hydrogen, covalent, ionic
Dipole-dipole interactions are the weakest because they are the result of attractions between weak partial charges
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of dipole-dipole interaction, but they are much stronger.
An ionic bond is the result of the complete transfer of electrons from on atom to another. This results in a positive charge on one atom and a negative charge on the other. The charges on these ions are much stronger than in dipoles. The two oppositely charged atoms are held together by electrostatic attraction.
Atoms that are part of a covalent bond share electrons. This makes the atoms harder to separate and, therefore, the bond is very strong.
Example Question #1 : Covalent Bonds
Which of these following diatomic molecules is joined by a double covalent bond?
Oxygen has a valence of 6, meaning it is looking to form two covalent bonds to complete its octet. Thus, 



Example Question #2 : Molecules And Compounds
Which of the following best explains the main difference between strong and weak acids or bases?
Strong acids and bases ionize completely in water whereas weak ones do not
Weak acids and bases dissociate completely in water
None of these
Strong acids and bases are more concentrated than weaker ones
Strong acids and bases always have multiple protons to donate or accept
Strong acids and bases ionize completely in water whereas weak ones do not
Molarity has no determination in whether an acid or base is strong or weak. Rather, molarity specifies the concentration of hydroxide or hydrogen ions in a solution. Weak Acids do not completely dissociate in water, while strong acids do. Polyprotic acids, those with more than one proton to donate, do not necessarily determine if an acid is strong (e.g. hydrochloric acid is an example of a strong, monoprotic acid).
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All College Chemistry Resources