All College Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #61 : Reactions
Determine the pH of a solution that is 
Since 

Thus, ![[H_3O^+]=0.40M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668813/gif.latex)
Recall how to find the pH of a solution:
Plug in the given hydronium ion concentration to find the pH of the given solution.
Remember to maintain the correct number of significant figures.
Example Question #62 : Reactions
Find the pH for a solution that is 


Start by assuming that there is 
Next, find the mass of 
Now, find the number of moles of 
Since we initially assumed that we had 

Since 

Recall how to find the pH of a solution.
Example Question #63 : Reactions
Find the pH of a solution that is 

Start by assuming that there is 
Next, find the mass of 
Now, find the number of moles of 
Since we initially assumed that we had 

Since 

Recall how to find the pH of a solution.
Example Question #1 : P H
Which of the following techniques will decrease the pH of a solution?
Decreasing the concentration of protons
Increasing the amount of Hydroxide molecules
Adding more acid at the same Molarity of the solution
Increasing the concentration of protons
Increasing the amount of solvent
Increasing the concentration of protons
Increasing the concentration of protons of a solution will make the solution more acidic; therefore, it lowers the solution’s pH. Decreasing the concentration of protons will make the solution more basic, raising the pH. Adding more acid of the same molarity of the original solution will not increase the concentration of protons and will not increase acidity or lower the pH. Increasing the amount of hydroxide ions will make the solution more basic and raise the pH. Increasing the amount of solvent will lower the concentration, affecting molarity and not lowering the pH.
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All College Chemistry Resources


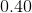


![\text{pH}=-\log([H_3O^+])](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668814/gif.latex)








![[\text{HBr}]=0.06491M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668764/gif.latex)
![[\text{HBr}]=[H_3O^+]=0.06491M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668767/gif.latex)
![\text{pH}=-\log([H_3O^+])](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668768/gif.latex)








![[\text{HI}]=0.3995M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668687/gif.latex)
![[\text{HI}]=[H_3O^+]=0.3995M](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668690/gif.latex)
![\text{pH}=-\log([H_3O^+])](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/668691/gif.latex)




