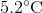All Physical Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Other Thermodynamic Principles
If a 

Possible Answers:
Correct answer:
Explanation:
The thermal energy an object contains is given by:
Where 
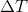
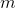


Plug in known values and solve:
Chisom
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
Georgia Southern University, Bachelor of Science, Biochemistry. University of Georgia, Current Grad Student, Pharmacy.
Noah
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
Northampton County Area Community College, Associate in Science, Biology, General. Northampton County Area Community College,...
All Physical Chemistry Resources
Physical Chemistry Tutors in Top Cities:
Atlanta Physical Chemistry Tutors, Austin Physical Chemistry Tutors, Boston Physical Chemistry Tutors, Chicago Physical Chemistry Tutors, Dallas Fort Worth Physical Chemistry Tutors, Denver Physical Chemistry Tutors, Houston Physical Chemistry Tutors, Kansas City Physical Chemistry Tutors, Los Angeles Physical Chemistry Tutors, Miami Physical Chemistry Tutors, New York City Physical Chemistry Tutors, Philadelphia Physical Chemistry Tutors, Phoenix Physical Chemistry Tutors, San Diego Physical Chemistry Tutors, San Francisco-Bay Area Physical Chemistry Tutors, Seattle Physical Chemistry Tutors, St. Louis Physical Chemistry Tutors, Tucson Physical Chemistry Tutors, Washington DC Physical Chemistry Tutors
Popular Courses & Classes
GMAT Courses & Classes in Dallas Fort Worth, GMAT Courses & Classes in Houston, SSAT Courses & Classes in Denver, GMAT Courses & Classes in New York City, GRE Courses & Classes in San Diego, GRE Courses & Classes in Washington DC, GRE Courses & Classes in San Francisco-Bay Area, SSAT Courses & Classes in Boston, ACT Courses & Classes in Phoenix, Spanish Courses & Classes in San Diego
Popular Test Prep
ACT Test Prep in Miami, ISEE Test Prep in Atlanta, GRE Test Prep in New York City, ACT Test Prep in Phoenix, LSAT Test Prep in Chicago, LSAT Test Prep in Phoenix, SSAT Test Prep in Dallas Fort Worth, LSAT Test Prep in Boston, ACT Test Prep in New York City, MCAT Test Prep in Washington DC