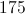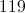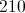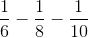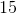All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1292 : Concepts
What is the perimeter of a right triangle with hypotenuse 

It cannot be determined from the information given.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the length of the second leg can be determined.
We are given the length of the hypotenuse and one leg.
The perimeter of the triangle is the sum of the lengths of the sides.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Perimeter Of A Right Triangle
Which of these polygons has the same perimeter as a right triangle with legs 6 feet and 8 feet?
A regular pentagon with sidelength one yard.
None of the other responses is correct.
A regular decagon with sidelength one yard.
A regular hexagon with sidelength one yard.
A regular octagon with sidelength one yard.
A regular octagon with sidelength one yard.
A right triangle with legs 6 feet and 8 feet has hypotentuse 10 feet, as this is a right triangle that confirms to the well-known Pythagorean triple 6-8-10. The perimeter is therefore 
We are looking for a polygon with this perimeter. Each choice is a polygon with all sides one yard long, so we want the polygon with eight sides - the regular octagon is the correct choice.
Example Question #1 : Right Triangles
The lengths of the legs of a right triangle are 






First, we need to use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Now, add up all three side lengths to find the perimeter of the triangle.
Example Question #4 : Properties Of Triangles
A right triangle has leg lengths of 

First, use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse.
Substituting in 



Now, add up the three sides to find the perimeter:
Example Question #5 : Properties Of Triangles
What is the perimeter of a right triangle with legs of length 

In order to find the perimeter 




Substituting in our known values:
Now that we have the lengths of all sides of the right triangle, we can calculate the perimeter:
Example Question #6 : Properties Of Triangles
What is the perimeter of a right triangle with a hypotenuse of length 

Not enough information provided
In order to find the perimeter 




Substituting in our known values:
Subtracting 
Now that we have the lengths of all three sides of the right triangle, we can calculate the perimeter 
Example Question #7 : Properties Of Triangles
Find the perimeter 


Not enough information provided
In order to find the perimeter 




Substituting in our known values:
Now that we have all three sides of the right triangle, we can calculate the perimeter:
Example Question #1 : Right Triangles
If a 

For the triangles to be similar, the dimensions of all sides must have the same ratio by dividing the 3-4-5 triangle.
The 6-8-10 triangle will have a scale factor of 2 since all dimensions are doubled the original 3-4-5 triangle.
The only correct answer that will yield similar ratios is the 
The other answers will yield different ratios.
Example Question #6 : Shape Properties
What is the main difference between a right triangle and an isosceles triangle?
A right triangle has to have a 

A right triangle has to have a 

A right triangle has to have a 

A right triangle has to have a 

An isosceles triangle has to have a 

A right triangle has to have a 

By definition, a right triangle has to have one right angle, or a 

Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of The Side Of A Right Triangle
A right triangle has a hypotenuse of 39 and one leg is 36. What is the length of the other leg?
You may recognize these numbers as multiples of 13 and 12 (each by a factor of 3) and remember that sides of length 5, 12 and 13 make a special right triangle. So the other leg would be 15 
If you don't remember this, you can use Pythagorean theorem:
All SSAT Upper Level Math Resources