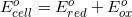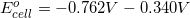All AP Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Cell Potential And Free Energy
1. 
2. 
3.
What is 
Possible Answers:




Correct answer:

Explanation:
There are two concepts to consider in this problem. First, the question asks for the 


Carolyn
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
University of Miami, Bachelor of Science, Biology, General. University of Alaska Fairbanks, Master of Science, Fishing and Fi...
All AP Chemistry Resources
Popular Subjects
Math Tutors in Washington DC, Reading Tutors in Los Angeles, Statistics Tutors in Denver, Statistics Tutors in Seattle, Calculus Tutors in San Diego, English Tutors in Dallas Fort Worth, SAT Tutors in Boston, Calculus Tutors in Denver, SSAT Tutors in San Francisco-Bay Area, LSAT Tutors in Houston
Popular Courses & Classes
GRE Courses & Classes in Denver, ISEE Courses & Classes in San Francisco-Bay Area, ISEE Courses & Classes in Boston, GMAT Courses & Classes in Philadelphia, Spanish Courses & Classes in San Diego, SSAT Courses & Classes in Atlanta, SSAT Courses & Classes in Houston, GMAT Courses & Classes in Denver, LSAT Courses & Classes in Chicago, GRE Courses & Classes in Philadelphia
Popular Test Prep
GRE Test Prep in Atlanta, GMAT Test Prep in Dallas Fort Worth, SAT Test Prep in Atlanta, MCAT Test Prep in Miami, SAT Test Prep in Dallas Fort Worth, ISEE Test Prep in Boston, GRE Test Prep in New York City, LSAT Test Prep in Dallas Fort Worth, ACT Test Prep in Los Angeles, LSAT Test Prep in San Diego