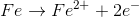All AP Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Reaction Types
What is the balanced equation when heptane is combusted?
C3H8 + 5 O2 → 4 H2O + 3 CO2
C7H16 + 11 O2 → 8 H2O + 7 CO2
C7H16 + O2 → H2O + CO2
C5H12 + 8 O2 → 6 H2O + 5 CO2
2 C7H14 + 5 O2 → 3 H2O + 6 CO2
C7H16 + 11 O2 → 8 H2O + 7 CO2
Heptane: C7H16. Combustion is when a molecule reacts with O2 and the products are CO2 and H2O. Balancing gives 7 CO2, 8 H2O, 1 heptane, and 11 O2
Example Question #1 : Reactions And Equilibrium
Which of the following reactions has the most exothermic heat of reaction?
The longer the hydrocarbon chain, the greater the amount of combustion products (CO2 and H20) generated. Branched molecules such as isopropane and isobutane are more difficult to combust than their straight-chain counterparts.
Example Question #1 : Reaction Types
Which of the following conditions would describe a combustion reaction?
Endergonic with a negative
Exothermic with a positive
Exothermic with a negative
Endothermic with a positive
Exergonic with a positive
Exothermic with a negative
An exothermic reaction will have a negative 

A combustion reaction releases heat; thus it must have a negative 
Exergonic reactions have a negative 
Example Question #1 : Oxidation Reduction Reactions
The following ReDox reaction takes place in acidic solution:
Fe2+ + Cr2O72– → Fe3+ + Cr3+
What is the sum of coefficients in this redox reaction?
33
36
37
35
34
36
When you balance the redox reaction in acidic conditons, there are 6Fe2+, 1 Cr2O72–, 14 H+, 6 Fe3+, 2 Cr3+, and 7 H2O. Don't forget to add the 1 in front of the Cr2O72–
Example Question #1 : Balancing Oxidation Reduction Reactions
For the following unbalanced redox reaction, how many electrons are transferred and which chemical species is being oxidized?
One electron is transferred; Hg is oxidized
Two electrons are transferred; P is oxidized
One electron is transferred; P is oxidized
Two electrons are transferred; Hg is oxidized
Two electrons are transferred; Hg is oxidized
To begin, we will need to separate the given reaction into the two half-reactions by identifying changes in oxidation number. In this case, mercury (Hg) and phosphorus (P) show a change in oxidation number. Mercury begins with an oxidation number of zero, and ends with an oxidation number of 



Now we can begin to look at the half-reactions.
Balance the atoms.
Now balance the electrons. We know that each mercury atom loses one electron and each fluorine atom gains one electron.
We can see that two electrons are tranferred. To identify the element being oxidized, we must find the element that is losing electrons. In this case, mercury is being oxidized.
Example Question #2 : Oxidation Reduction Reactions
How many electrons are involved in the following reaction?
1 e-
3 e-
4 e-
5 e-
2 e-
5 e-
The common factor between 1 e- and 5 e- is 5. Therefore the number of electrons involved is 5 e-.
Example Question #3 : Oxidation Reduction Reactions
How many electrons are involved in the following reaction?
1 e-
4 e-
2 e-
5 e-
10 e-
10 e-
The common factor between 2 e- and 5 e- is 10. Therefore the number of electrons involved is 10 e-.
Example Question #1 : Balancing Oxidation Reduction Reactions
What is the balanced coefficient on OH- for the following reaction:

1
5
4
3
2
2
Add them together:
Simplify:
Add Hydroxides to each side to counter H+.
Simplify:
Example Question #3 : Oxidation Reduction Reactions
What is the sum of all the balanced coefficients in the following reaction:

12
14
8
16
10
14
Add the equations together
Simplify
Add 2 OH- to each side to cancel out the H+.
Simplify:
Example Question #4 : Oxidation Reduction Reactions
For the redox reaction shown, which of the following half reactions occurs in the anode?
Recall that oxidation always occurs at the anode (in both the electrochemical and galvanic cells). 



Certified Tutor
All AP Chemistry Resources