All ISEE Upper Level Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Use A Venn Diagram

Refer to the above Venn diagram.
Define universal set 
Define sets 

Which of the following numbers is an element of the set represented by the gray area in the diagram?
The gray area represents the set of all elements that are in 



104 is the correct choice.
Example Question #2 : How To Use A Venn Diagram

In the above Venn diagram, the universal set is defined as 
What is 








Example Question #3 : How To Use A Venn Diagram

In the above Venn diagram, the universal set is defined as 

















Example Question #4 : How To Use A Venn Diagram

In the above Venn diagram, the universal set is defined as 














Example Question #5 : How To Use A Venn Diagram
The following Venn diagram depicts the number of students who play hockey, football, and baseball. How many students play football and baseball?

The number of students who play football or baseball can by finding the summer of the number of students who play football alone, baseball alone, baseball and football, and all three sports.
Example Question #2 : Data Analysis And Probability
A class of 
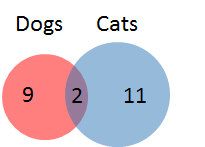
First, calculate the number of students with a dog:
Next, subtract the number of students with a dog from the total number of students.
Certified Tutor
All ISEE Upper Level Math Resources





































