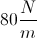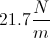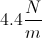All MCAT Physical Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #22 : Work, Energy, And Power
A spring in a pinball machine is compressed 


The energy in a spring is given by the equation 


The kinetic energy in the pinball is found using the equation 
Now that we have kinetic energy, we can find the equal energy that was stored in the spring to begin.
Example Question #21 : Work, Energy, And Power
A 2kg mass is attached to a massless spring with force constant 100N/m. The system rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the spring is compressed 5cm, then released, what is the maximum velocity of the mass?
50cm/s
10.2cm/s
35.4cm/s
12.5cm/s
25cm/s
35.4cm/s
Use conservation of energy to compare the point of maximum compression and the point of maximum velocity. At maximum compression, all energy is spring potential energy, where 


Plugging in the given information for Es and solving for v gives the following series of calculations:
Example Question #1 : Potential Energy (Gravitational And Spring)
If a ball is attached to a spring that has a spring constant of 20N/m and is compressed 0.1m, what is the total energy of the oscillation?
The total energy of a simple harmonic oscillating system can be determined by the equation 
Example Question #1 : Potential Energy (Gravitational And Spring)
A massless spring rests horizontally on a table, with its right end attached to a 


Use conservation of energy to equate the initial spring potential energy and the final kinetic energy:
The initial situation is defined when the spring and block are compressed, and the final situation is defined to be when the block moves back through the equilibrium point. For a spring, the potential energy is maximal when the spring is compressed and the kinetic energy is maximal when the mass passes equilibrium. We can set up a equation based on these factors.
Use the equations for spring potential energy and for kinetic energy to incorporate the appropriate variables into the equation.
We are given values for the displacement, mass, and final velocity. Using these values, we can isolate the spring constant.
Example Question #1 : Potential Energy (Gravitational And Spring)
A block with mass, 


The spring potential is given by the equation 

When 
Example Question #51 : Newtonian Mechanics And Motion
A certain chocolate candy bar contains 

Our first step is to convert kilocalories to Joules.
Now that we have converted to standard units, we can use the formula for gravitational potential energy to find the height.
We know our energy limit from the candy bar, the mass of the barbell, and the gravitational acceleration.
Solve to isolate the height.
Note that we end up with kilometers because we used kilojoules in our calculation.
Example Question #1 : Potential Energy (Gravitational And Spring)
A 2kg mass is suspended on a rope that wraps around a frictionless pulley attached to the ceiling with a mass of 0.01kg and a radius of 0.25m. The other end of the rope is attached to a massless suspended platform, upon which 0.5kg weights may be placed. While the system is initially at equilibrium, the rope is later cut above the weight, and the platform subsequently raised by pulling on the rope.

After the rope is cut and the platform falls, we want to pull the platform back up to 5m above the ground. How much energy is required to raise the platform?
98J
50J
200J
75J
98J
First, we need to understand what type of energy we are considering. As the resistive force to motion is due to gravity, we are talking about gravitational potential energy. We need to use the formula U = mgh.
Plugging in the values that are provided, we can solve for the potential energy (U).
U = (2kg)(9.8m/s2)(5m) = 98J
The amount of work required is equal to the change in potential energy of the platform.
Example Question #221 : Mcat Physical Sciences
Two students (student X and student Y) lift a boulder vertically from point A to point B. Student X directly lifts the boulder from point A to point B, whereas student Y uses a pulley to lift the boulder. This allows student Y to apply a force (

The vertical distance between point A and point B is 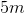
Student Z uses an inclined plane to lift the boulder and exerts only one third of 
I. The change in potential energy
II. The distance travelled
III. The sum of the change in kinetic energy and change in potential energy
I and III
I and II
II only
I only
II only
The change in potential energy is defined as:
This means that the potential energy is only dependent on the change in vertical height, which is the same for both students. Since both students travel the same distance, the change in potential energy is equal and statement I is true.
Student X directly lift the boulder whereas student Z uses an inclined plane. Student Z slides the boulder along a larger distance than student X, even if their total displacement ends up begin equal; therefore, statement II is false.
Recall that the sum of change in kinetic energy and change in potential energy is equal to work, which is the same for both students (work is path independent in a gravitational field). The total work for both students will be equal, and statement III will be true.
The only statement that is not equal for both students is statement II.
Example Question #1 : Potential Energy (Gravitational And Spring)
A 2kg lead ball is loaded into a spring cannon and the cannon is set at a 45º angle on a platform. The spring has a spring constant of 100N/m and the ball and spring system is compressed by 1m before launch. While the ball is in flight air resistance can be neglected, and the ball finishes its flight by landing at a cushion placed some distance away from the cannon.
How much energy is stored in the spring before the ball is launched?
20kJ
50kJ
20J
50J
50J
In order to determine how much energy is stored, we first need to understand what type of energy we want to consider. A spring stores potential energy; the potential energy of the spring is maximized at maximal displacement from its resting state. In order to compute the potential energy stored, we need both the spring constant (100N/m) and the displacement from resting (1m).
PEs = ½k(Δx)2 = ½(100N/m)(1m)2 = 50J
Example Question #2 : Potential Energy (Gravitational And Spring)
Two children are playing with sleds on a snow-covered hill. Sam weighs 50kg, and his sled weighs 10kg. Sally weighs 40kg, and her sled weighs 12kg. When they arrive, they climb up the hill using boots. Halfway up the 50-meter hill, Sally slips and rolls back down to the bottom. Sam continues climbing, and eventually Sally joins him at the top.
They then decide to sled down the hill, but disagree about who will go first.
Scenario 1:
Sam goes down the hill first, claiming that he will reach a higher velocity. If Sally had gone first, Sam says they could collide.
Scenario 2:
Sally goes down the hill first, claiming that she will experience lower friction and thus reach a higher velocity. If Sam had gone first, Sally says they could collide.
Scenario 3:
Unable to agree, Sam and Sally tether themselves with a rope and go down together.
How much potential energy does Sally have at the top of the hill on her sled?
260000J
26kJ
26,000kJ
260J
2.6kJ
26kJ
This is a tricky question only because you have to keep your units straight. The formula is simply PE = mgh.
PE = 52kg * 10m/s2 * 50m = 26,000J = 26kJ
Certified Tutor
All MCAT Physical Resources