All Organic Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Help With Aldehyde And Ketone Synthesis
What reagents are required to undergo Swern oxidation?
Dichloromethane, trimethylamine, and DMS
Diethyl ether, organometallic compound, and H3O+
COCl2, triethylamine, and DMSO
SOCl2, pyridine, and triethylamine
Pyridine, DMSO, and HCOOH
COCl2, triethylamine, and DMSO
Swern oxidation requires COCl2, triethylamine, and DMSO. The same reaction can be accomplished using PCC and dichloromethane. This reaction oxidizes an alcohol to a carbonyl, but only works with primary and secondary alcohols.
Example Question #1 : Help With Aldehyde And Ketone Synthesis

Which of the following reactions will result in the given product?
D
A
E
B
C
C
The starting material first needs to be brominated, which occur at the tertiary carbon. Then, an elimination reaction needs to take place to form an alkene intermediate, which will transpire through the E2 pathway with the tertbutoxide ion in tertbutanol. After this, an alcohol needs to be formed through hydroboration because we need the carbonyl group on the less subsituted carbon. After an alcohol is formed, the PCC reaction can oxidize the alcohol to make it a carbonyl. All these reactions are shown in choice C.
Example Question #12 : Reactions By Product
A compound, 


What is the original compound?
4-chloro-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
None of the other answers
2-chloro-1,3-dimethylcylopentane
1-chloro-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane
2-chloro-1,1-dimethylcyclopentane
2-chloro-1,3-dimethylcylopentane
In the first step of the reaction, a chlorine is abstracted and a double bond is formed. In the ozonolysis step, the molecule is broken at the double bond and each carbon at that bond gets double bonded to an oxygen. The presence of zinc keeps it from becoming a carboxylic acid.
Working backwards, you must remove the oxygens from the final product and redraw the molecule at the double bond. This intermediate is 1,3-dimethylcyclopentene. Next, the chlorine must be added to one of the carbons on the double bond. The only possible choice is 2-chloro-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane.
Example Question #2 : Help With Aldehyde And Ketone Synthesis

Which of the following reagents is required to produce the ketone product?
In order to convert a secondary alcohol into a ketone, we must employ 
Example Question #1 : Help With Ether And Ester Synthesis
Which of the following reactions is NOT a valid synthesis of methyl benzoate?
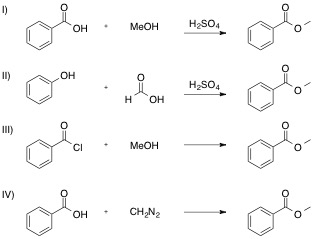
I
All are valid syntheses of methyl benzoate
II
III
IV
II
Each reaction is shown, with its name and correct product below.
If you are unsure how the product is obtained through each reaction, use your textbook or internet sources to find a mechanism for each. Reactions I, II, and III are specific examples of substitution reactions, and the last, reaction IV, goes through a more complex addition-elimination reaction to release nitrogen gas.
Working through the mechanism for a reaction is always a certain way to find the product, even if you don't know from the outset what it will be. Just look for the electrophile and nucleophile in each step of the mechanism, and push those arrows!

Example Question #611 : Organic Chemistry

What reagent is required to complete the reaction?
4-toluenesulfonyl chloride (TsCl)
HBr
NaH
PCC
Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4)
4-toluenesulfonyl chloride (TsCl)
This reaction is completed by tosylating the hydroxyl group to make it a good leaving group (keep in mind the stereochemistry is retained through the tosylation reaction). The second step is an SN2 reaction with the methoxide ion, which gives the correct stereochemistry. HBr will not result in the correct stereochemical product.
Example Question #2 : Help With Ether And Ester Synthesis
What is the product of the reaction between sodium ethoxide and 1-bromopropane?
None of these
1-ethoxypropane
No reaction occurs
2-ethoxypropane
1-propanol
1-ethoxypropane
In solution, the sodium in sodium ethoxide will ionize and an 
Bromine is a good leaving group. In the same step, the bromine leaves and the electrons from the ethoxide will attack that carbon. This creates a bond between the carbon and an oxygen.
The final product is an ether with three carbons on one side and two on the other. This is 1-ethoxypropane.
Example Question #2 : Help With Ether And Ester Synthesis
An organic chemist wants to synthesize an ether product. She begins with methanol and ethanol as her substrates. How would she go about synthesizing the desired ether product?
Convert the alcohol on the methanol to a tosylate group and allow this modified substrate to react with the ethanol
Add heat to the substrates to elicit a dehydration reaction
Put both substrates in an aprotic solvent and allow them to react via
It is impossible to create an ether product with these substrates
Convert the alcohol on the methanol to a tosylate group and allow this modified substrate to react with the ethanol
The substrates must be modified in order to attain the desired product. In order to get the desired product, she needs to change one of the alcohol groups into a good leaving group. One way to do this is to react the methanol with 
Example Question #2 : Help With Ether And Ester Synthesis
Consider the following reaction.


In this reaction, two molecules of an alpha-hydroxy acid are condensed with heat to form product. What functional group is created in this reaction?
Ketone
Ether
Aldehyde
Ester
Ester
For this question, we're shown the structures of both the reactants and products, and we're asked to identify which functional group is in the product.
First, let's go through the answer choices and define them. Then, we'll compare that definition with what we see in the product.
Aldehydes are functional groups in which a carbon atom is double bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbon atom must also be bound to at least one hydrogen atom, and to another hydrogen or carbon atom. Usually, aldehydes occur at the terminal ends of a molecule.
Ketones are similar to aldehydes. These functional groups contain a carbon atom double bound to an oxygen atom. In addition, the carbon atom is bound to two other carbon atoms. Thus, ketones tend to be found within a compound, as opposed to at the terminal ends.
Ethers are a class of functional group in which an oxygen atom is situated between two carbon atoms via a single bond.
Carboxylic acids are a functional group in which a carbon is double bound to one oxygen atom, and also single bonded to the oxygen of a hydroxyl group. This functional group does not occur in the product, but it does occur in the reactant.
Esters are a functional group in which a carbon atom is double bonded to an oxygen atom, and also single bonded to another oxygen atom. However, unlike carboxylic acids, esters do not contain a hydroxyl group. Instead, the oxygen atom is bound to another "R group," typically another carbon atom.
Now, let's go ahead and take a look at the product. Shown in red circles, we see that there are two ester groups in the product. Thus, the ester functional group is the correct answer.

Example Question #2 : Carbonyl Products
Which of the following reactions would NOT produce a carboxylic acid?
PCC is considered a weak oxidizing agent. The reaction of a primary alcohol with PCC would only yield an aldehyde, while reaction with a secondary alcohol will yield a ketone. PCC will not be used to generate carboxylic acids.
A stronger oxidation, like 

Certified Tutor
All Organic Chemistry Resources
















