All SAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Circles

Figure not drawn to scale.
In the figure above, circle C has a radius of 18, and the measure of angle ACB is equal to 100°. What is the perimeter of the red shaded region?
36 + 20π
36 + 36π
36 + 10π
18 + 36π
18 + 10π
36 + 10π
The perimeter of any region is the total distance around its boundaries. The perimeter of the shaded region consists of the two straight line segments, AC and BC, as well as the arc AB. In order to find the perimeter of the whole region, we must add the lengths of AC, BC, and the arc AB.
The lengths of AC and BC are both going to be equal to the length of the radius, which is 18. Thus, the perimeter of AC and BC together is 36.
Lastly, we must find the length of arc AB and add it to 36 to get the whole perimeter of the region.
Angle ACB is a central angle, and it intercepts arc AB. The length of AB is going to equal a certain portion of the circumference. This portion will be equal to the ratio of the measure of angle ACB to the measure of the total degrees in the circle. There are 360 degrees in any circle. The ratio of the angle ACB to 360 degrees will be 100/360 = 5/18. Thus, the length of the arc AB will be 5/18 of the circumference of the circle, which equals 2πr, according to the formula for circumference.
length of arc AB = (5/18)(2πr) = (5/18)(2π(18)) = 10π.
Thus, the length of arc AB is 10π.
The total length of the perimeter is thus 36 + 10π.
The answer is 36 + 10π.
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of An Arc

In the circle above, the angle A in radians is
What is the length of arc A?
Circumference of a Circle =
Arc Length
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Length Of An Arc
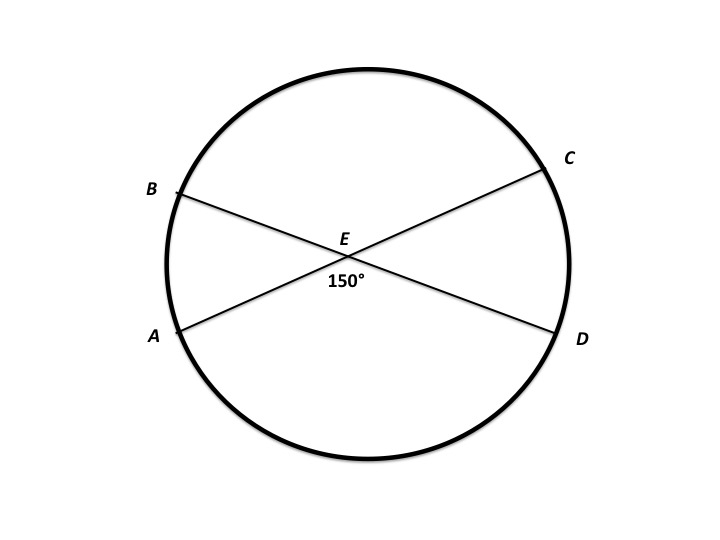
In the figure above, 




The formula for arclength is 
You know that 



Since

the sum the lengths of arcs 


Example Question #2 : How To Find The Length Of An Arc

Figure NOT drawn to scale
Refer to the above figure. Evaluate 


Setting 

All SAT Math Resources





























