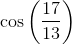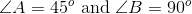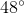All ACT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Triangles
The measure of 3 angles in a triangle are in a 1:2:3 ratio. What is the measure of the middle angle?
The angles in a triangle sum to 180 degrees. This makes the middle angle 60 degrees.
Example Question #51 : Plane Geometry
A 17 ft ladder is propped against a 15 ft wall. What is the degree measurement between the ladder and the ground?
Since all the answer choices are in trigonometric form, we know we must not necessarily solve for the exact value (although we can do that and calculate each choice to see if it matches). The first step is to determine the length of the ground between the bottom of the ladder and the wall via the Pythagorean Theorem: "x2 + 152 = 172"; x = 8. Using trigonometric definitions, we know that "opposite/adjecent = tan(theta)"; since we have both values of the sides (opp = 15 and adj = 8), we can plug into the tangential form tan(theta) = 15/8. However, since we are solving for theta, we must take the inverse tangent of the left side, "tan-1". Thus, our final answer is
Example Question #241 : Geometry
What is the sine of the angle between the base and the hypotenuse of a right triangle with a base of 4 and a height of 3?
By rule, this is a 3-4-5 right triangle. Sine = (the opposite leg)/(the hypotenuse). This gives us 3/5.
Example Question #1 : Triangles
In a right triangle ABC, the measure of angle C is greater than 60 degrees. Which of the following statements could describe the measures of angles A and B?
Given that it is a right triangle, either angle A or B has to be 90 degrees. The other angle then must be less than 30 degrees, given that C is greater than 60 because there are 180 degrees in a triangle.
Example:
If angle C is 61 degrees and angle A is 90 degrees, then angle B must be 29 degrees in order for the angle measures to sum to 180 degrees.
Example Question #4 : Right Triangles
Right triangle 

Solving this problem quickly requires that we recognize how to break apart our ratio.
The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of all interior angles in a triangle is 
Since this is true, we can assume that 


Thus, 
To find the value of one angle of the ratio, simply assign fractional value to the sum of the ratios and multiply by 

Thus, the shortest angle (the one represented by 

Example Question #5 : Right Triangles
Right triangle 

The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of all interior angles in a triangle must be 


The rest is simple subtraction:
Thus, our missing angle is 
All ACT Math Resources