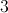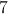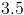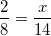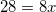All High School Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
What is the area of a kite with diagonals of 5 and 7?
To find the area of a kite using diagonals you use the following equation 
That diagonals (

Plug in the diagonals for 

Then multiply and divide to get the area.
The answer is
Example Question #2 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
Find the area of the following kite:

The formula for the area of a kite is:
Where 

Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #3 : How To Find The Area Of A Kite
Find the area of the following kite:

The formula for the area of a kite is:
where 

Use the formulas for a 





Our 
Our 
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : How To Find The Perimeter Of Kite
Find the perimeter of the following kite:

In order to find the length of the two shorter edges, use a Pythagorean triple:
In order to find the length of the two longer edges, use the Pythagorean theorem:
The formula of the perimeter of a kite is:
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #4 : Quadrilaterals
Find the perimeter of the following kite:

The formula for the perimeter of a kite is:
Where 

Use the formulas for a 





Our 
Our 
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : Trapezoids
When polygons are similar, the sides will have the same ratio to one another. Set up the appropriate proportions.
Cross multiply.
Example Question #6 : Quadrilaterals
Find the area of the following trapezoid:

The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
Where 


To find the height of the trapezoid, use a Pythagorean triple:
Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #7 : Quadrilaterals
Find the area of the following trapezoid:

Use the formula for 
The formula is:
Where 

Beginning with the 



Creating another 



The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
Where 


Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #8 : Quadrilaterals
Determine the area of the following trapezoid:

The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:

where 


Plugging in our values, we get:
Example Question #1 : Trapezoids
Find the area of the following trapezoid:

The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:

where 


Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the height of the trapezoid:
Plugging in our values, we get:
All High School Math Resources




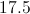











































 .
.