All SAT II Chemistry Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Reactions And Equilibrium
Which of the following cannot act as a Bronsted-Lowry base (proton recipient) in aqueous solution?



Example Question #2 : Reactions And Equilibrium
A scientist makes a solution by adding 0.2 grams of 






Example Question #1 : Oxidation State
What is the oxidation number of nitrogen in 
First, note that the molecule does not have a charge, meaning that the oxidation numbers of each atom must add up to zero. Hydrogen has an oxidation number of 





Example Question #1 : Oxidation State
The following is a modified true/false question. In it, you must decide if each individual statement is true (T) or false (F). If both are true, then you must also decide if the second statement is a correct explanation (CE) of the first statement.
I: An 

BECAUSE
II: reduction is a loss of electrons
T, T (Statement II is not a correct explanation of Statement I)
T, F
F, F
T, T, CE
F, T
T, F
Statement II is false: reduction is a gain of electrons. Looking at statement I, the ion's charge would decrease by 3 in becoming a metal, which suggests that the ion gains 3 electrons. Thus, it is undergoing reduction.
Example Question #1 : Chemical Equilibrium
What is an expression for the equilibrium constant for the above equation?
The formula for the equilibrium constant is the product of the concentration of the products divided by the product of the concentration of the reactants. Since none of the reactants or products have coefficients, no exponents are needed in the expression. The phases do not affect the equilibrium constant in this example.
Certified Tutor
All SAT II Chemistry Resources







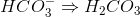












![\frac{[H_2CO_3]}{[CO_2][H_2O]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1073981/gif.latex)
![\frac{[H_2CO_3]}{[CO_2]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1073982/gif.latex)
![\frac{[H_2O]}{[H_2CO_3][CO_2]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1073984/gif.latex)
![\frac{[H_2CO_3]^3}{[H_2O]^2[CO_2]^2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1073985/gif.latex)
![\frac{[CO_2][H_2O]}{[H_2CO_3]}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/1073983/gif.latex)



