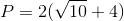All ISEE Lower Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : Coordinate Geometry

The parallelogram shown above has a height of 






To find the area of the parallelogram apply the formula:
Since, the paralleogram has a base of 

Example Question #2 : Coordinate Geometry

The parallelogram shown above has a height of 

In order to find the correct perimeter of the parallelogram apply the formula: 


In order to find the length of side 





Thus, the solution is:
Therefore,
Example Question #3 : Coordinate Geometry

Identify the coordinate points for the parallelogram that is shown above.
In order to identify the coordinate points for this parallelogram, notice that there must be two different pairs of coordinates with the same 
Thus, the parallelogram has coordinate points:
Example Question #4 : Coordinate Geometry

What is the area of the parallelogram shown above?





To find the area of the parallelogram that is shown, apply the formula:
Since the parallelogram has a base of 

Example Question #5 : Coordinate Geometry

Given that the above parallelogram has base sides with a length of 

In order to find the perimeter of the parallelogram apply the formula: 


In this problem, 

Thus, the correct answer is:
Example Question #6 : Coordinate Geometry

Identify the coordinate points for the parallelogram shown above.
In order to identify the coordinate points for this parallelogram, notice that there must be two different pairs of coordinates with the same 
Thus, the correct set of coordinates is:
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Rectangle On A Coordinate Plane
A shape is plotted on a coordinate axis. The endpoints are 
Square
Trapezoid
Parallelogram
Rectangle
Triangle
Rectangle
Plot the points on a coordinate axis. Once it's graphed, you can see that there are two pairs of congruent, or equal, sides. The shape that best fits these characteristics is a rectangle.
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Rectangle On A Coordinate Plane

Rectangle 










In order to find the area of rectangle 
Since rectangle 



Example Question #3 : How To Find A Rectangle On A Coordinate Plane

Rectangle 




To find the perimeter of rectangle 
Thus, the solution is:
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Rectangle On A Coordinate Plane
Rectangle 










The area of rectangle 
To find the length of the rectangle compare the x values of two of the coordinates:
Since 

To find the width of the rectangle we need to look at the y coordinates of two of the points.
Since 

The solution is:
All ISEE Lower Level Quantitative Resources