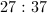All ISEE Lower Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Ratio
Stacy has started collecting coins. She has twice as many wheat pennies as she does 1946 dimes, and three times as many 1983 quarters as she does 1946 dimes. If Stacy has 
We know that Stacy has 
We also know that she has twice as many wheat pennies, so we must multiply 

We also know that Stacy has three times as many 1986 quarters, so we multiply 

Now our ratio of wheat pennies to 1986 quarters is 

So our ratio becomes
Example Question #2 : How To Find A Ratio
Cassie works a four hour shift at the coffee shop. During her shift, 


Since there are 

The second number of our ratio is 

Therefore, our ratio is :
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Ratio
Steve is having a birthday party. So far, he has invited thirty-nine of his friends from school, fifteen of whom are girls. He wants to make the ratio of girls to boys at the party two to one. How many more girls does he need to invite, assuming no more boys are invited?
Counting Steve, there are forty attendees so far, fifteen of whom are girls and twenty-five of whom (including Steve) are boys. To obtain a two-to-one girl to boy ratio, he needs to invite a total of fifty girls, so he needs to invite thirty-five more.
Example Question #4 : How To Find A Ratio
Scott's mother bakes 12 cookies and he eats half of them. Scott's mom then puts red frosting on 4 cookies and blue frosting on the rest of the cookies. What is the ratio of cookies with red frosting to cookies with blue frosting?
If Scott's mother bakes 12 cookies and he eats half of them, that means he will eat 6 cookies, leaving 6 uneaten cookies.
If Scott's mom then puts red frosting on 4 cookies and blue frosting on the rest of the cookies, 2 cookies will get blue frosting. (
Therefore, the ratio of cookies with red frosting to cookies with blue frosting is 

Example Question #2 : Ratio And Proportion
For every 3 peanuts in a bag of trail mix, there are 1 chocolate chip and 2 raisins. What is the proportion of raisins in the mix?
Given that there are 3 peanuts for every 1 chocolate chip and 2 raisins, the proportion of raisins can be found by dividing the number of raisins by the sum of all the items in the mix. This results in:

Therefore, 
Example Question #5 : How To Find A Ratio
Jose is 






The ratio of Jose to Michael's height is 
Thus, if Jose is 

We can write this as the expression, 
Also, an equivalent ratio for 

Example Question #6 : How To Find A Ratio
Find an equivalent ratio.
An equivalent ratio of 

This is the furthest simplification of the ratio.
The greatest common divisor is needed to simplify the expression.
Both 




Thus, the correct answer is 
Example Question #1 : How To Find A Ratio
Solve for 
To solve this problem the relationship between the two numbers in the first ratio needs to be established.
Since, 


Thus, 



Thus,
Example Question #3 : Ratio And Proportion
There are 

First, find the number of boys in the class by subtracting the number of girls in the class from the total number of students.
Now, we know that the ratio of the number of boys in the class to the total number of students in the class is 
We can express that ratio as the following fraction:
Example Question #6 : How To Find A Ratio
There are 

First, find the number of girls in the class by subtracting the number of boys in the class from the total number of students.
Now, we know that the ratio of the number of boys in the class to the total number of students in the class is 
We can express that ratio as the following fraction:
Certified Tutor
Certified Tutor
All ISEE Lower Level Quantitative Resources